The Coca-Cola Company: Difference between revisions
(Business Model) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Executive Summary == | |||
{{Infobox company | {{Infobox company | ||
| name = The Coca-Cola Company | | name = The Coca-Cola Company | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
}} | }} | ||
The Coca-Cola Company, a beverage company, manufactures, markets, and sells various nonalcoholic beverages worldwide. The company provides sparkling soft drinks; flavored and enhanced water, and sports drinks; juice, dairy, and | The Coca-Cola Company, a beverage company, manufactures, markets, and sells various nonalcoholic beverages worldwide. The company provides sparkling soft drinks; flavored and enhanced water, and sports drinks; juice, dairy, and plant based beverages; tea and coffee; and energy drinks. It also offers beverage concentrates and syrups, as well as fountain syrups to fountain retailers, such as restaurants and convenience stores. The company sells its products under the Coca-Cola, Diet Coke/Coca-Cola Light, Coca-Cola Zero Sugar, Fanta, Fresca, Schweppes, Sprite, Thumbs Up, Aquarius, Ciel, Dasani, glacéau smart water, glacéau vitamin water, Ice Dew, I LOHAS, Powerade, Topo Chico, AdeS, Del Valle, fair life, innocent, Minute Maid, Minute Maid Pulpy, Simply, Ayataka, BODYARMOR, Costa, FUZE TEA, Georgia, and Gold Peak brands. It operates through a network of independent bottling partners, distributors, wholesalers, and retailers, as well as through bottling and distribution operators. The company was founded in 1886 and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. | ||
== History Of Coca-Cola == | == History Of Coca-Cola == | ||
| Line 52: | Line 53: | ||
Over time, the Coca-Cola Company shifted their focus towards sustainability and environmental responsibility, taking important steps to reduce its carbon footprint and promote recycling efforts. It also explored new markets and remained on track with emerging trends, such as entering the promising market for ready-to-drink teas and coffees | Over time, the Coca-Cola Company shifted their focus towards sustainability and environmental responsibility, taking important steps to reduce its carbon footprint and promote recycling efforts. It also explored new markets and remained on track with emerging trends, such as entering the promising market for ready-to-drink teas and coffees | ||
== Business Model == | |||
[[File:Cocacola Business Model.jpg|thumb]] | |||
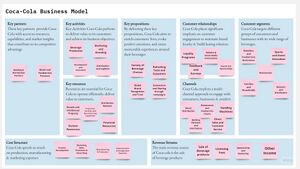
Coca-Cola's products encompass a wide spectrum, including carbonated soft drinks, juices, bottled water, sports drinks, and ready-to-drink teas and coffees. These beverages are sold under various well-known brands, such as Coca-Cola, Diet Coke, Sprite, Minute Maid, and Powerade, catering to a broad spectrum of consumer preferences and needs. | |||
Coca-Cola's value creation begins with its extensive network of suppliers, which provide the necessary raw materials like sweeteners, flavorings, and packaging materials. The company leverages its strong relationships with these suppliers to ensure consistent quality and availability of ingredients. Once the products are manufactured, Coca-Cola employs an intricate distribution system that spans both developed and emerging markets. This distribution network plays a crucial role in efficiently reaching retailers, restaurants, vending machines, and other outlets, ensuring widespread accessibility to its beverages. Coca-Cola's iconic branding and extensive marketing campaigns further enhance its value proposition by creating strong consumer recognition and loyalty. By tailoring its products to meet diverse tastes and offering convenient access, Coca-Cola successfully generates value by fulfilling the refreshment and hydration needs of consumers worldwide. | |||
Revision as of 11:21, 4 August 2023
Executive Summary
 Coca-Cola headquarters in Atlanta | |
| Type | Public |
|---|---|
| ISIN | [https://stockhub.co/index.php?title=Toollabs:isin/&language=en&isin=US1912161007 US1912161007] |
| Industry | Beverage |
| Founded | January 29, 1892 Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. |
| Founders |
|
| Headquarters | , U.S. |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people |
|
| Brands | List of Coca-Cola brands |
| Revenue | |
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
| Owners |
|
Number of employees | |
| Subsidiaries | List of the Coca-Cola Company subsidiaries |
| Website | |
The Coca-Cola Company, a beverage company, manufactures, markets, and sells various nonalcoholic beverages worldwide. The company provides sparkling soft drinks; flavored and enhanced water, and sports drinks; juice, dairy, and plant based beverages; tea and coffee; and energy drinks. It also offers beverage concentrates and syrups, as well as fountain syrups to fountain retailers, such as restaurants and convenience stores. The company sells its products under the Coca-Cola, Diet Coke/Coca-Cola Light, Coca-Cola Zero Sugar, Fanta, Fresca, Schweppes, Sprite, Thumbs Up, Aquarius, Ciel, Dasani, glacéau smart water, glacéau vitamin water, Ice Dew, I LOHAS, Powerade, Topo Chico, AdeS, Del Valle, fair life, innocent, Minute Maid, Minute Maid Pulpy, Simply, Ayataka, BODYARMOR, Costa, FUZE TEA, Georgia, and Gold Peak brands. It operates through a network of independent bottling partners, distributors, wholesalers, and retailers, as well as through bottling and distribution operators. The company was founded in 1886 and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia.
History Of Coca-Cola
The history of Coca-Cola is truly rich and fascinating. The distinguished beverage was invented in 1886 in Atlanta, Georgia, USA by pharmacist Dr. John S. Pemberton who envisioned it as a remedy for various ailments. Pemberton's bookkeeper, Frank M. Robinson, is credited with devising the iconic name of the beverage “Coca-Cola” and its signature script.
In 1888, Asa Candler, a businessman and pharmacist, acquired the rights to Coca-Cola's formula and embarked on an ambitious journey to promote and expand the brand. Through innovative marketing techniques, Candler transformed Coca-Cola into a popular beverage, appealing to a broader consumer base. He introduced tactics such as distributing free drink coupons and displaying Coca-Cola signage on buildings, effectively establishing the brand's visibility.
In 1919, the Coca-Cola Company was sold to a group of investors, led by Ernest Woodruff and his son Robert W. Woodruff. As president and chairman of the firm, Robert W. Woodruff’s run from the 1920s to the 1950s proved transformative for the company. Under his leadership, Coca-Cola international presence boomed through establishing bottling plants and distribution networks across the globe.
During World War II, Coca-Cola forged a successful collaboration with the American military by distributing drinks to soldiers as part of the firm's commitment to supporting the army. This further solidified Coca-Cola's status as a symbol of American culture and patriotism.
In the following years, Coca-Cola continued to diversify its product portfolio through introducing Diet Coke in 1982, which became an instant success and remains a popular choice for health-conscious consumers. Furthermore, Coca-Cola expanded its beverage offerings by acquiring multiple brands including Sprite, Fanta, Minute Maid, Power play, and Dasani.
Over time, the Coca-Cola Company shifted their focus towards sustainability and environmental responsibility, taking important steps to reduce its carbon footprint and promote recycling efforts. It also explored new markets and remained on track with emerging trends, such as entering the promising market for ready-to-drink teas and coffees
Business Model
Coca-Cola's products encompass a wide spectrum, including carbonated soft drinks, juices, bottled water, sports drinks, and ready-to-drink teas and coffees. These beverages are sold under various well-known brands, such as Coca-Cola, Diet Coke, Sprite, Minute Maid, and Powerade, catering to a broad spectrum of consumer preferences and needs.
Coca-Cola's value creation begins with its extensive network of suppliers, which provide the necessary raw materials like sweeteners, flavorings, and packaging materials. The company leverages its strong relationships with these suppliers to ensure consistent quality and availability of ingredients. Once the products are manufactured, Coca-Cola employs an intricate distribution system that spans both developed and emerging markets. This distribution network plays a crucial role in efficiently reaching retailers, restaurants, vending machines, and other outlets, ensuring widespread accessibility to its beverages. Coca-Cola's iconic branding and extensive marketing campaigns further enhance its value proposition by creating strong consumer recognition and loyalty. By tailoring its products to meet diverse tastes and offering convenient access, Coca-Cola successfully generates value by fulfilling the refreshment and hydration needs of consumers worldwide.