Summary
BAE Systems plc provides defense, aerospace, and security solutions worldwide. The company operates through five segments: Electronic Systems, Cyber & Intelligence, Platforms & Services (US), Air, and Maritime. The Electronic Systems segment offers electronic warfare systems, navigation systems, electro-optical sensors, military and commercial digital engine and flight controls, precision guidance and seeker solutions, military communication systems and data links, persistent surveillance systems, space electronics, and electric drive propulsion systems. The Cyber & Intelligence segment provides solutions to modernize, maintain, and test cyber-harden aircraft, radars, missile systems, and mission applications that detect and deter threats to national security; systems engineering, integration, and sustainment services for critical weapons systems, C5ISR, and cyber security; and solutions and services to intelligence and federal/civilian agencies. It also offers data intelligence solutions to defend against national-scale threats, protect their networks, and data against attacks; security and intelligence solutions to the United Kingdom government and allied international governments; anti-fraud and regulatory compliance solutions; and enterprise-level data and digital services. The Platforms & Services (US) segment manufactures combat vehicles, weapons, and munitions, as well as provides ship repair services and the management of government-owned munitions facilities. The Air segment develops, manufactures, upgrades, and supports combat and jet trainer aircraft. The Maritime segment designs, manufactures, and supports surface ships, submarines, torpedoes, radars, and command and combat systems; and supplies naval gun systems. It also supplies naval weapon systems, missile launchers, and precision munitions. The company was founded in 1970 and is based in Farnborough, the United Kingdom.
Operations
Company History
Mission Statement
Corporate Strategy[1]
BAE Systems has a corporate strategy that builds on their vision and mission. It is comprised of six key long-term areas of focus that will help BAE achieve their vision and mission. It is centred on maintaining and growing their core franchises and securing growth opportunities through advancing their three strategic priorities.
1. Sustain and grow their defence and security businesses
- Deliver on commitments effectively and efficiently
- Develop offerings to meet the future defence and security needs
2. Continue to grow their business in adjacent markets
- Take capabilities into adjacent attractive markets
- Develop dual-use opportunities delivering civil solutions to leverage back to meet challenges for defence customers
3. Develop and expand their international business
- Mature international activities, broadening offerings to established customers
- Develop relations with additional customers
4. Inspire and develop a diverse workforce to drive success
- Ensure diversified thinking and harness the full potential of people
- Create an environment and proposition in which people will thrive
- Seek opportunities to drive efficiency, standardisation and synergies
- Identify opportunities for higher-margin offerings
6. Advance and integrate their sustainability agenda
- Emphasise the vital role played in protecting countries and civilians and supporting communities
- Progress the delivery of their decarbonisation strategy
Priorities
Serving as a bridge between the long-term strategy and short term objectives, are the strategic priorities. These priorities have been successfully demonstrated by BAE Systems.
- Drive operational excellence
- BAE Systems has been part of the F-35 programme since its inception, bringing our expertise into the development, advanced manufacture, electronic warfare systems and sustainment of the world’s largest defence programme. Led by the US, with participation from the UK, Italy, Netherlands, Australia, Canada, Denmark and Norway, this collaborative programme delivers a stealthy, multi-role combat aircraft capable of operating from land and sea to nations across the globe. As a key partner, BAE collaborates with the programme’s prime contractor, Lockheed Martin, to deliver around 15% of each aircraft (excluding propulsion), playing a major role in the development, production and sustainment of each jet.
- Continuously improve competitiveness and efficiency
- To improve production efficiency and increase capacity, BAE has embarked on the process of constructing a new, modern ship lift/ land-level ship repair complex at our Jacksonville, Florida shipyard. Once it is fully operational, the complex will feature a ship lift that can easily move vessels in excess of 25,000 tons, and the new land-level repair complex will enable the team to work on three or more ships simultaneously parked ashore with access to their hulls. The $200m (£166m) investment will bring a 300% increase to the shipyard’s current dry-docking capacity and expand the shipyard’s customer diversity by bringing in more commercial work.
- Advance and further leverage our technology
- BAE Systems is working with partners to design and deliver a new flying combat air demonstrator, which will play a critical role in the delivery of the UK’s Future Combat Air System. The flagship project is part of a suite of novel technologies being developed by Team Tempest, which will see BAE Systems engineers lead the design, test, evaluation and build process and bring together new digital engineering technologies. The first flight of the demonstrator is set to take place within the next five years.
Segments
Key programmes and franchises
Revenue by segments
Current Projects
ESG
Environmental
Social
Governance
Market
Total Addressable Market:
Here, the total addressable market (TAM) is the global defence market which is valued at $2.24 trillion based on worldwide military expenditure figures for 2022[2].
Serviceable Available Market:
Here, the serviceable available market (SAM) is the defence market in select geographical regions (shown in map) accessible to the company which is valued at $1.37 trillion based on the respective 2022 military expenditure figures[2].
Serviceable Obtainable Market:
Here, the serviceable obtainable market (SOM) is the defence market in select geographical regions (shown in map) accessible to the company which is valued at $1.28 trillion according to the 2022 BAE Systems Annual Report[2].
Region Accessible:
USA
UK
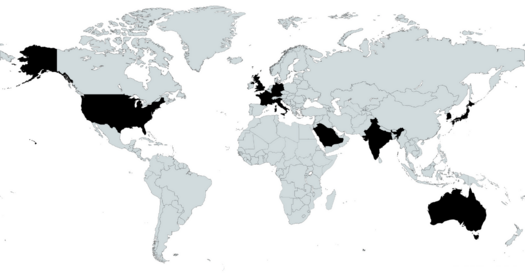
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Australia
India
France
Germany
South Korea
Japan
Italy
Largest Region:
USA
Market Drivers:
- Invasion of Ukraine and tensions in East Asia drive increased spending.
- Increased spending by Japan in response to perceived growing threats from China, North Korea and Russia.
- Aids and grants to Ukraine
Market Trends:
- Unmanned combat vehicles
- Autonomous fighter jets
- Edge computing
- 3D printed technology
- Use of AI in defence equipment
Competition
Competitive Advantages:
- World class defence capabilities across multiple domains - air, land, sea and undersea
- Strong customer relationships - largest defence supplier in the UK and Australia, and among top ten in the US
- Diversified Business Portfolio - wide range of mission critical electronic systems including electronic warfare systems, flight and engine controls, night vision systems, surveillance and reconnaissance sensors, and power and energy management system.
Competitors:
| Company Name | HQ | Founding Year | No. of Employees | Revenue (FY 2022) | Market Cap. |
| BAE Systems | Farnborough, United Kingdom | 1999 | 93000 | $26.3B | $29.6B |
| Lockheed Martin Corporation | Bethesda, Maryland, United States | 1995 | 116000 | $66.0B | $113.3B |
| Northrop Grumman Corp | Falls Church, Virginia, United States | 1994 | 95000 | $36.6B | $65.3B |
| General Dynamics | Reston, Virginia, United States | 1952 | 106500 | $39.4B | $61.3B |
| The Boeing Company | Arlington, Virginia, United States | 1916 | 156000 | $66.6B | $136.5B |
| RTX (Raytheon) | Arlington County, Virginia, United States | 1922 | 182000 | $67.1B | $125.4B |
Leadership
Executive Team
Ownership Structure
Financials
Most recent half
| Income Statement (£m) | H1 2023 | H1 2022 | % change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 10997 | 9739 | 12.9% |
| Operating Income / EBIT | 1233 | 1028 | 19.9% |
| Net Income | 1005 | 647 | 55.3% |
The first half of 2023 saw a 12.9% growth in the total revenue generated, resulting in subsequent growths in operating income and net income. This comes after a £1.8bn contract from the Czech Republic to produce 246 CV90 MkIV infantry fighting vehicles. The Air sector also saw continuation with the Qatar Typhoon and Hawk programmes.
Historical data - 5 years
| Income Statement - (£m) | FY-22 | FY-21 | FY-20 | FY-19 | FY-18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 21258 | 19521 | 19277 | 18305 | 16821 |
| Gross Profit | 14063 | 12468 | 12413 | 11803 | 10898 |
| Gross Margin | 66% | 64% | 64% | 64% | 65% |
| EBITDA | 2846 | 2545 | 2384 | 2259 | 1874 |
| Operating Income / EBIT | 2384 | 2389 | 1930 | 1899 | 1605 |
| Net Income | 1674 | 1912 | 1371 | 1532 | 1033 |
| Balance sheet - (£m) | FY-22 | FY-21 | FY-20 | FY-19 | FY-18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total assets | 31462 | 27135 | 27530 | 25630 | 24746 |
| Total liabilities | 20062 | 19467 | 22609 | 20119 | 19128 |
| Net assets | 11400 | 7668 | 4921 | 5511 | 5618 |
Details
Financial forecast / projection - 5 years
| Income Statement - (£m) | FY-23 | FY-24 | FY-25 | FY-26 | FY-27 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 24688 | 26076 | 27735 | 28967 | 29832 |
| Gross Profit | 15980 | 16878 | 17952 | 18749 | 19309 |
| Gross Margin | 65% | 65% | 65% | 65% | 65% |
| EBITDA | |||||
| Operating Income / EBIT | 2424 | 2534 | 2668 | 2758 | 2810 |
| Net Income |
Details
Valuation
Intrinsic Valuation (DCF)
Expected Return on Investment
The Stockhub users estimate that the expected return of an investment in BAE Systems plc over the next five years is 31%. This value was arrived at through the use of an intrinsic valuation in the form of a discounted cash flow model.
Assuming that a suitable return level of five years is 10% per year (based of the S&P 500 returns) and BAE Systems achieves its return level of 31%, then the company can be considered as undervalued.
Assumptions
| Description | Value | Commentary |
|---|---|---|
| Valuation Model | Discounted Cash Flow Model | One form of intrinsic valuation is the discounted cash flow model where future cash flows are discounted to the present value.
Research has suggested that to estimate the expected return of an investment over a long-term investment horizon, a discounted cash flow model provides an accurate projection. |
| Financial Projections | Stockhub, CapitalIQ, Yahoo Finance | To improve the reliability of financial projections, a mixture of sources was used when projecting key financial metrics such as revenue. |
| Discount Rate | WACC | The weighted average cost of capital was used as the discount rate as it expresses the return that both bondholders and shareholders demand to provide the company with capital. The cost of equity and cost of debt have been calculated in the tables provided below using values taken from the company's financial statements, beta for the stock, and expected market returns. |
Free cashflow calculation
| Current Share Price: £9.68 | |||||||||||||
| £ million | Historical | Projected | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | |
| Income Statement | |||||||||||||
| Revenue | 16787 | 17790 | 17224 | 16821 | 18305 | 19277 | 19521 | 21258 | 24688 | 26076 | 27735 | 28967 | 29832 |
| % growth | 6% | -3% | -2% | 9% | 5% | 1% | 9% | 16% | 6% | 6% | 4% | 3% | |
| Cost Of Goods Sold | 7101 | 7212 | 6085 | 5923 | 6502 | 6864 | 7053 | 7195 | 8708 | 9198 | 9783 | 10218 | 10523 |
| % of revenue | 42% | 41% | 35% | 35% | 36% | 36% | 36% | 34% | 35% | 35% | 35% | 35% | 35% |
| Gross Profit | 9686 | 10578 | 11139 | 10898 | 11803 | 12413 | 12468 | 14063 | 15980 | 16878 | 17952 | 18749 | 19309 |
| gross margin | 58% | 59% | 65% | 65% | 64% | 64% | 64% | 66% | 65% | 65% | 65% | 65% | 65% |
| Selling General & Admin Exp. | 5200 | 5838 | 6229 | 6203 | 6457 | 6681 | 6640 | 7431 | 8509 | 8988 | 9559 | 9984 | 10282 |
| % of revenue | 31% | 33% | 36% | 37% | 35% | 35% | 34% | 35% | 34% | 34% | 34% | 34% | 34% |
| Depreciation & Amort. | 351 | 333 | 263 | 269 | 511 | 543 | 513 | 549 | 553 | 584 | 621 | 648 | 668 |
| % of revenue | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 3% | 3% | 3% | 3% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| Amort. Of Goodwill and Intangibles | 0 | 0 | 82 | 78 | 101 | 128 | 188 | 215 | 272 | 313 | 361 | 406 | 447 |
| % of revenue | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 2% |
| Other Operating Expense | 2872 | 2929 | 3032 | 2821 | 3087 | 3348 | 3283 | 3786 | 4222 | 4459 | 4743 | 4954 | 5101 |
| % of revenue | 17% | 16% | 18% | 17% | 17% | 17% | 17% | 18% | 17% | 17% | 17% | 17% | 17% |
| Total Operating Expenses | 8072 | 8767 | 9261 | 9024 | 9544 | 10029 | 9923 | 11217 | 12731 | 13447 | 14302 | 14938 | 15384 |
| Operating Income/ EBIT | 1263 | 1478 | 1533 | 1527 | 1647 | 1713 | 1844 | 2082 | 2424 | 2534 | 2668 | 2758 | 2810 |
| EBITDA | 1614 | 1811 | 1878 | 1874 | 2259 | 2384 | 2545 | 2846 | 3248 | 3431 | 3649 | 3811 | 3925 |
| Tax Expense | 147 | 213 | 216 | 191 | 94 | 225 | 198 | 315 | 295 | 308 | 325 | 336 | 342 |
| Effective tax rate | 12% | 14% | 14% | 13% | 6% | 13% | 11% | 15% | 12% | 12% | 12% | 12% | 12% |
| EBIAT | 1116 | 1265 | 1317 | 1336 | 1553 | 1488 | 1646 | 1767 | 2129 | 2226 | 2343 | 2422 | 2468 |
| Cashflow | |||||||||||||
| D&A | 351 | 333 | 263 | 269 | 511 | 543 | 513 | 549 | 553 | 584 | 621 | 648 | 668 |
| % of revenue | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 3% | 3% | 3% | 3% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| Amort. Of Goodwill and Intangibles | 0 | 0 | 82 | 78 | 101 | 128 | 188 | 215 | 272 | 313 | 361 | 406 | 447 |
| % of revenue | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 2% |
| Capital Expenditure | -359 | -408 | -389 | -358 | -360 | -385 | -516 | -599 | -741 | -782 | -832 | -869 | -895 |
| % of revenue | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 3% | 3% | 3% | 3% | 3% | 3% | 3% |
| Change in NWC | 717 | 108 | 640 | 192 | 422 | -196 | -95 | 132 | 521 | 550 | 585 | 611 | 630 |
| % of revenue | 4% | 1% | 4% | 1% | 2% | -1% | 0% | 1% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| Unlevered FCF | 391 | 1082 | 633 | 1133 | 1383 | 1970 | 1926 | 1800 | 1692 | 1790 | 1907 | 1996 | 2059 |
Notes on projections
Revenue projections were adapted from Capital IQ's estimates, and cross-checked with Yahoo Finance.
The COGS margin was projected by taking the average of COGS margins from 2017 onwards, as there seems to have been a stabilisation after this year.
The Selling General & Admin Expenses, Depreciation and Amortisation, Other Operating Expenses and the Tax Expenses were projected by applying average of each respective margin over the historical period and applying it to each forecast year.
Amortisation of Goodwill and Intangibles was projected as growing from 1.1% to 1.5% to model the steady increase in its margin seen in the historical period.
- Note: Upon cross-check with BAE System's Annual Report, Capital IQ presents the true depreciation expense as "Depreciation and Amortisation", and the true Amortisation Expense as "Amortisation of Goodwill and Intangibles".
Capital Expenditure was taken as having a steady 3% margin, seen from the recent step up in its value (2021, 2022)
Change in NWC was projected by taking the average of the non-negative margins from the historical data, and applying this average as the margin for each forecast year.
Calculation of the discount rate (WACC)
| WACC | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
| Weights | ||
| Total Debt | 6610 | |
| Market Cap | 29363 | |
| Total | 35973 | |
| Wd | 18% | Weight of debt calculated as the total debt as a proportion of total capital. |
| We | 82% | Weight of equity calculated as the market cap as a proportion of total capital |
| Debt | ||
| Total Debt | 6610 | Cost of debt was calculated by taking interest expenses from the income statement and dividing this by the total debt making note of the fact that debt is a tax deductable item. |
| Interest Expense | -233 | |
| Rate | 3.5% | |
| Effective Tax Rate | 12% | |
| Rd(1-t) | 3.1% | |
| Equity | ||
| Risk Free Rate | 4.05% | Capital asset pricing model was used to calculate the cost of equity. Risk free rate of the US Treasury 10 Year was used. |
| Beta | 0.57 | Beta for the stock was found from Yahoo Finance |
| Market Rate | 10% | Current market rate was calculated as the average returns of the S&P 500 over the past 50 years. |
| Re | 7.4% | |
| Discount Rate | 6.6% | This is the value used for the WACC |
| Perpetuity Growth Rate | 2.0% | A perpetuity growth rate of 2% was used as this is sufficiently low to ensure that the company is not projected to increase in size far faster than the global economy in the very long term. |
Cashflow projection
| £ millions | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | Terminal Value (Perpetuity Growth) | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1692 | 1790 | 1907 | 1996 | 2059 | 45229 | The terminal value of the company was calculated using the Gordon Growth Model.[5] | ||
DCF
| Present Value of FCF | 7769 |
|---|---|
| Terminal Value | 45229 |
| Net Present Value of TV | 32791 |
| Enterprise Value | 40559 |
| Net Debt | 1866 |
| Equity Value | 38693 |
| Shares Out | 3050 |
| Equity Value per Share | £12.69 |
| Current share price | £9.68 |
| Difference | 31% |
Sensitivity Analysis
A sensitivity analysis was also conducted to reflect how changes in the discount rate and perpetuity growth rate would affect the intrinsic value of the company.
| £12.69 | Perpetuity Growth | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0% | 1.5% | 2.0% | 2.5% | 3.0% | ||
| WACC | 5.5% | £13.61 | £15.12 | £17.07 | £19.66 | £23.30 |
| 6.0% | £12.17 | £13.36 | £14.84 | £16.75 | £19.30 | |
| 6.5% | £10.99 | £11.95 | £13.11 | £14.57 | £16.44 | |
| 6.6% | £10.69 | £11.59 | £12.69 | £14.04 | £15.77 | |
| 7.0% | £10.01 | £10.79 | £11.73 | £12.87 | £14.30 | |
| 7.5% | £9.18 | £9.83 | £10.60 | £11.51 | £12.64 | |
| 8.0% | £8.47 | £9.02 | £9.65 | £10.40 | £11.31 | |
Relative Valuation
Expected Return on Investment
The Stockhub users estimate that the expected return of an investment in BAE Systems plc over the next five years is 15%. This value was arrived at through the use of a relative valuation method in the form of a comparable company analysis.
Assuming that BAE Systems achieves its return level of 15%, then the company can be considered as undervalued.
Comparable company analysis
| Market Data | Financials | Valuation Ratios | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company | Ticker | Share Price | Currency | Shares Out /millions | Equity Value /millions | Net Debt /millions | Enterprise Value /millions | EPS | Revenue /millions | EBITDA /millions | Net Income /millions | EV/Revenue | EV/EBITDA | P/E | ||
| BAE Systems plc | LSE: BA | 9.62 | GBP | 3050 | 29341 | 3406 | 32747 | 0.50 | 22516 | 2776 | 1941 | 1.45 | 11.80 | 19.24 | ||
| Rolls-Royce Holdings plc | LSE: RR | 2.56 | GBP | 8362 | 21408 | 3732 | 25140 | 0.25 | 19665 | 2180 | 1514 | 1.28 | 11.53 | 10.24 | ||
| Safran SA | ENXTPA: SAF | 155.98 | EUR | 420 | 65527 | -81 | 65447 | 8.00 | 24065 | 4477 | 3166 | 2.72 | 14.62 | 19.50 | ||
| Thales S.A. | ENXTPA: HO | 140.78 | EUR | 209 | 29353 | 915 | 30267 | 6.08 | 19607 | 2499 | 1203 | 1.54 | 12.11 | 23.15 | ||
| Leonardo S.p.a. | BIT: LDO | 13.95 | EUR | 575 | 8025 | 4110 | 12135 | 1.62 | 16347 | 1536 | 857 | 0.74 | 7.90 | 8.61 | ||
| Airbus SE | ENXTPA: AIR | 137.79 | EUR | 789 | 108744 | -4661 | 104083 | 5.33 | 67010 | 7702 | 3872 | 1.55 | 13.51 | 25.85 | ||
| Northrop Grumman Corporation | NYSE: NOC | 430.17 | USD | 151 | 65085 | 13726 | 78811 | 30.23 | 37881 | 7243 | 4649 | 2.08 | 10.88 | 14.23 | ||
| Hensoldt AG | XTRA: 5UH | 31.63 | EUR | 105 | 3321 | 632 | 3953 | 0.80 | 1904 | 251 | 77 | 2.08 | 15.74 | 39.54 | ||
| Dassault Aviation societe anonyme | ENXTPA: AM | 185.32 | EUR | 79 | 14640 | -8190 | 6451 | 10.61 | 6850 | 733 | 806 | 0.94 | 8.80 | 17.47 | ||
| Rheinmetall AG | XTRA: RHM | 271.23 | EUR | 43 | 11771 | 828 | 12599 | 11.71 | 7175 | 1004 | 474 | 1.76 | 12.55 | 23.16 | ||
| L3Harris Technologies, Inc. | NYSE: LHX | 181.48 | USD | 189 | 34318 | 9158 | 43476 | 4.19 | 17988 | 2760 | 802 | 2.42 | 15.75 | 43.31 | ||
| Raytheon | NYSE: RTX | 85.47 | USD | 1460 | 124786 | 31532 | 156318 | 3.74 | 70573 | 12088 | 5562 | 2.21 | 12.93 | 22.85 | ||
| BAE Systems plc valuation | EV/Revenue | EV/EBITDA | P/E |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Comparable Ratio | 1.76 | 12.39 | 22.54 |
| Revenue | 22516 | NA | NA |
| EBITDA | NA | 2776 | NA |
| EPS | NA | NA | 0.5 |
| Implied Enterprise Value | 39553 | 34404 | NA |
| Net Debt | 3406 | 3406 | NA |
| Implied Equity Value | 36147 | 30998 | NA |
| Shares Outstanding | 3050 | 3050 | NA |
| Implied Value Per Share | 11.85 | 10.16 | 11.27 |
| Average | £11.09 | ||
| Current Share Price | £9.68 | ||
| Difference | 14.6% | ||
Risks[1]
BAE Systems believes that managing risks effectively is key to successfully delivering on their strategies and strategic priorities. They employ a thorough, multifaceted, top to bottom risk management framework, which aims to mitigate any risk to their strategy that is identified. The Board has the overall responsibility, advised by the Audit, ESG and Executive Committees. The basis of the framework is:
Identify, Analyse, Evaluate, Mitigate
All risks primarily affect their future revenue and financial health.
Government customers, defence spending and terms of trade risks
These risks affect strategies 1, 2, 3, 5
- 95% of sales in 2022 were in defence. Government expenditure on defence can vary based on policy, politics, budgetary constraints as well as national security threats, and some governments have already faced constraints. However, BAE has a geographically well-spread market, many countries within which have announced plans to defence spending in response to the currently elevated global threats. BAE also benefits from a large order backlog, as well as establishment with long-term projects.
- BAE systems faces threats to their ability to secure and maintain government contracts. Financial reviews can lead to budgetary reconsiderations and premature termination of contracts. However, BAE is established as being a major contributor to the industrial capabilities of the countries within its market.
- BAE also faces a risk with the fact that its cashflows depend on the timing and success in being awarded contracts as well as when they receive the corresponding cash. Not receiving cashflow on time can lead to an inability to focus on their own expenditure without requiring external funding - impacting credit rating. However, BAE manages their balance sheet conservatively, to ensure flexibility, as well as monitoring liquidity to ensure the retrieval of cash needed for operations.
International market risks
These risks affect strategies 1,2,3,5
- The risks of operating in international markets include: social and political changes impacting the business environment, economic downturns, political instability and civil disturbances, the imposition of restraints on the movement of capital, the introduction of burdensome taxes or tariffs, change of export control, tax and other government policy and regulations in the UK, US and all other relevant jurisdictions, and the inability to obtain or maintain the necessary export licences. Similar to the risk on fluctuations in government expenditure, BAE has a geographically well-spread market, many countries within which have announced plans to defence spending in response to the currently elevated global threats. BAE also benefits from a large order backlog, as well as establishment with long-term projects.
- They are exposed to volatility arising from movements in currency exchange rates, particularly in respect of the US dollar, euro, Saudi riyal and Australian dollar. There has been volatility in currency exchange rates in 2022.
- Brexit can still affect BAE System's ability to participate in, and receive contracts for, European Union-funded projects. However, BAE has a major role in certain European programmes, such as the Eurofighter, and is also supporting the UK government in maintaining the UK's role in European security and defence.
Contract risk, execution and supply chain risks
These risks affect strategies 1,2,4,5
- There is a risk associated with the costs of fixed-price contracts exceeding the contract amount, and hence resulting in a local loss. The price is agreed based on a projection of the inflation rate, and hence is subject to fluctuation. It is important for BAE systems to maintain tight tolerances on quality, time and cost, in a reliable, predictable and repeatable manner. They have also limited fixed-price contracts regarding design and development, which tend to have more associated risk.
- Like any business associated with product manufacturing. BAE system relies on its supply chain, which has intrinsic risk. There are lead-time and availability issues, as well as pricing pressures from inflationary increases in labour, energy and key materials.
Cyber security risks
These risks affect strategies 1,3,4
- Cyber threats can cause business and operational disruption. BAE Systems faces risks potential cybersecurity threats in the form of:
- Attacks impacting availability of its information technology and operational technology infrastructure and systems
- Attempts to gain access to or delete proprietary and classified information, of BAE Systems as well as its customers, partners and suppliers.
These threats are mitigated through constant monitoring, as well as cyber security training for its personnel.
Competition in international markets
These risks affect strategies 1,3,5
- BAE systems need to be able to win contracts for new and high-quality programmes, while depending on UK and US government support. However, their multi-market and international presence, balanced business portfolio and their capable and reliable track record of delivery is a factor that combats this risk. BAE systems also invests in research and development, to ensure cutting-edge technology that puts them in line with, or ahead of, the competition.
Outbreak of contagious disease
These risks affect strategies 1,2,3,4,5
- Similar to that of COVID-19, new pandemics can cause sever disruption to its operations, as well as its market. However, having been through the coronavirus pandemic, it is expected that the experience in dealing with such an event can minimise the impact of future pandemics, experience including safe working practices and effectively implementing working from home.
Climate change and the environment
These risks affect strategies 1,2,3,4,5,6
- BAE systems could face rigorous environmental laws and regulations, regarding air emissions, waste handling, use and handling of hazardous materials, remediation of soil and groundwater, contamination and the prevention of pollution through greenhouse gas emission. This could affect operations, as well as an ability to sell. Harsh environmental conditions could directly affect operations, through natural disasters and accidents arising from the environment. Furthermore, the adjustment to a low-carbon economy could mean increased tariffs and compliance costs, as well as a potentially reduced demand base, driven by politics and morality. However, BAE systems are working towards the target of achieving net zero across operations by 2030.
Laws and regulations
These risks affect strategies 1,2,3,4,5,6
- Their operations are within a highly regulated environment across multiple jurisdictions, and is therefore subject to regulations related to import-export controls, money laundering, false accounting, anti-bribery and anti-boycott provisions. It is crucial that BAE systems maintains responsible business and financial practices. They may also be affected by export restrictions, affecting their ability to sell their products.
Acquisitions
These risks affect strategies 1,2,3,5
- BAE Systems believes in the virtue of investing in value-enhancing acquisitions, where such an acquisition brings them closer to their strategised goals. They must ensure successful migration and integration of acquired business, as well as perform post-acquisition monitoring of its expected benefits
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 https://investors.baesystems.com/~/media/Files/B/BAE-Systems-Investor/documents/bae-ar-complete-2022-new.pdf
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 https://www.sipri.org/sites/default/files/2023-04/2304_fs_milex_2022.pdf
- ↑ https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/5720994/defense-global-market-opportunities-and
- ↑ https://www.baesystems.com/en/our-company/about-us
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/terms/t/terminalvalue.asp