Summary
- Bitcoin is a form of a digital currency that aims to eliminate the need for banks or governments. Alternatively, Bitcoin uses blockchain technology to support peer-to-peer transactions between users on a decentralised network [1].
- Launched in 2009, Bitcoin was the first and remains the most valuable, entrant in the emerging class of assets known as cryptocurrecy.
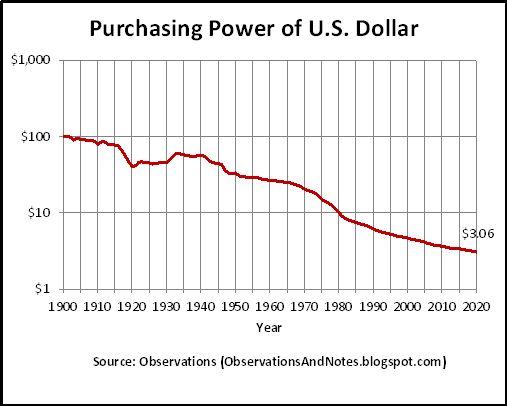
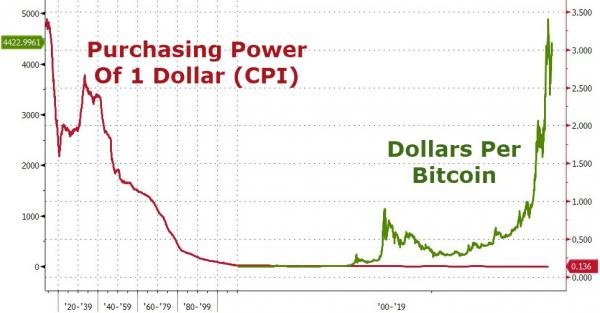
- Bitcoin is a currency. Research suggests that the most popular cryptocurrency will maintain its purchasing power for much longer than any other currency. In other words, the cryptocurrency will be a much better currency.
- Assuming Bitcoin's share of the money supply increases to 10% (from 2.2%) and the value of the global money supply remains unchanged (at $35.2 trillion), then that equates to a Bitcoin price of $167,619 per coin (from $41,458), and upside of 4x.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a currency.
What's unique about Bitcoin?
What makes Bitcoin unique is that it operates on a decentralised network (i.e. without the need of a central entity, such as the Bank of England), and the supply of the currency is limited (at 21 million coins).
The main benefit of operating on a decentralised network (rather than a centralised network) is that within the network, there is no single point of failure. In a centralised network, if the central entity that operates the network fails, then the whole network - and the currency that operates on the network - fails (i.e. there is a single point of failure in the network), whereas in a decentralised network, because there is no central entity, there is no single point of failure, and therefore the network - and currency - is likely to last for much longer, possibly forever.
For example, the world's first ever known currency is the Mesopotamian shekel, and it was operated by a central entity (The Kingdom of Lydia). When the central entity failed, so did the currency.
Another key benefit of transacting on a decentralised network is that transaction costs are likely to be lower.
Other factors that make Bitcoin unique:
- It's money, but digital (Although bitcoin is purely digital, it meets every classical definition of what makes something money. Instead of relying on physical properties (like gold and silver) or central authorities (like government-issued fiat currencies), bitcoin relies on the world’s most powerful computer network to mathematically enforce the rules that make it the first truly digital form of cash [2]
- There's a limited supply. There will never be more than 21 million Bitcoins. The creation of new bitcoin is mathematically defined and strictly enforced by the bitcoin network
- Bitcoin comes with the convenience of online banking and payment processing.
- Bitcoin has never been hacked.
- Bitcoin complements existing financial institutions. Globally, around 1.7 billion adults have no access to banking services [3]. However, because Bitcoin is unbiased, open, and public, it can serve communities that conventional financial institutions overlook, helping grow economies and creating economic mobility where it never existed.
How does Bitcoin work?
Each Bitcoin is a digital asset that can be stored at a cryptocurrency exchange or in a digital wallet [4]. Each individual coin represents the value of Bitcoin’s current price, but you can also own partial shares of each coin. The smallest denomination of each Bitcoin is called a Satoshi, sharing its name with Bitcoin’s creator (Satoshi Nakamoto). Each Satoshi is equivalent to a hundred millionth of one Bitcoin, so owning fractional shares of Bitcoin is quite common.
- Blockchain: Bitcoin is powered by open-source code known as blockchain, which creates a shared public history of transactions organized into "blocks" that are "chained" together to prevent tampering. This technology creates a permanent record of each transaction, and it provides a way for every Bitcoin user to operate with the same understanding of who owns what [5].
- Private and public keys: A Bitcoin wallet consists of a public key and private key, which work together to allow the owner to initiate and digitally sign transactions. This lets the user carry out the main purpose of Bitcoin - securely and safely transferring ownership from one user to another.
- Bitcoin mining: Validating transaction information and maintaining the integrity of the blockchain is bitcoin mining's main purpose, Bitcoin mining is the process of validating the information in a blockchain block by generating a cryptographic solution that matches specific criteria. When a correct solution is reached, a reward in the form of bitcoin and fees for the work done is given to the miner who reached the solution first [6]
Competition
| Item | Bitcoin | US Dollar |
|---|---|---|
| Does the currency operate on a decentralised network? | Yes | No |
| Is the supply of the currency limited? | Yes | No |
| How likely is the currency to act as a store of value? | High | Low |
| Item | Bitcoin | US Dollar |
|---|---|---|
| Medium of exchange | Yes | Yes |
| Measure of value | Yes | Yes |
| Standard of deferred payment | Yes | Yes |
| Store of value | Yes | No |
| Item | Bitcoin | Ether | XRP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Does the currency operate on a decentralised network? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Is the supply of the currency limited? | Yes | No | No |
| Is the cryptocurrency the most popular one? | Yes | No | No |
| How likely is the currency to act as a store of value? | High | Low | Low |
Other Cryptocurrencies
- Ethereum: [7]
- Bitcoin's larger competitor
- Second largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization
- Biggest platform for decentralised applications
- Seen as a general purpose blockchain
- Uses either, its platform-specific cryptographic token
2. Bitcoin cash: [8]
- One of the first alcoins that emerged and successfully traded off from bitcoin
- Made to resolve issues between bitcoin developers and miners
- Growing market capitalization
3. Tether: [9]
- One of the first stablecoins (cryptocurrencies that peg their market value to a specific currency in order to reduce volatility of the cryptocurrency)
- Smooths out price fluctuations
- Tether's price is directly tied to the U.S. dollar
4. XRP:
- XRP is the native token for the XRP ledger which Ripple created as a payment system.
5. Binance Coin (BNB)[10]
- Utility cryptocurrecy that operates as a payment method associated with trading on the Binance Exchange.
- Third largest-cryptocurrency by market capitalization
- Those who use the token as payment for exchange can trade with a discount price.
6. USD Coin (USDC)
- Pegs its price to the U.S. dollar
- Makes USDC a regulated stablecoin
7. Cardano: [11]
- One of the most fundamentally strong and best Bitcoin alternatives in the market
- Low transaction fees and continued developments
8. Solana:
- Outperformed the majority other cryptocurrencies (performs many more transactions per second than Ethereum)
- Charges lower transaction fees than Etheruem
- Designed to support decentralized applications
- Cryptocurrency running on the Solana blockchain is called Solana
9. Dogecoin: [12]
- The coin, which uses an image of the Shiba Inu as its avatar, is accepted as a form of payment by some major companies.
- Accepted as a payment model in sports teams and in AMC theatres.
10. Tron:
- Basic unit of accounts on the Tron blockchain
Market Capitalization
Major Cryptoassets By Percentage of Total Market Capitalization (Bitcoin Dominance Chart) - 2023 [13] and Market Capitalisation in terms of billions of dollars [14]
| Market Capitalisation (%) | Market Capitalisation ($ billions) | |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | 48.47% | 582.24 |
| Ethereum | 19.12% | 229.32 |
| Tether | 6.89% | 83.75 |
| XRP | 3.09% | 42.54 |
| BNB | 3.22% | 37.16 |
| USD Coin | 2.25% | 26.92 |
| Cardano | 0.94% | 10.94 |
| Solana | 0.91% | 10.65 |
| Dogecoin | 0.83% | 9.82 |
| TRON | 0.60% | 7.19 |
| Others | 13.69% | N/A |
Valuation
The total value of narrow money globally is estimated at $35.2 trillion as at May 2020, according to The Money Project.
The total value of Bitcoin as of today (20th March 2022) is $787 billion[1].
Accordingly, Bitcoin's share of the global money supply is 2.2%.
Bitcoin currently trades at $41,458[1] and the maximum number of coins is 21 million.
Assuming Bitcoin's share of the money supply increases to 10% (from 2.2%) and the value of the global money supply remains unchanged (at $35.2 trillion), then that equates to a Bitcoin price of $167,619 per coin (from $41,458), and upside of 4x.
Actions
To invest in Bitcoin, click here.
References