| Type | Decentralized blockchain |
| Release date | 30 July 2015 |
| Founder | Vitalik Buterin |
| Native cryptocurrency | Ether (ETH) |
| Mining method | Proof of stake (PoS) |
| Website | ethereum.org |
What is Ethereum?
- Ethereum is a globally distributed network of computers that is powered by blockchain technology[1].
- The Ethereum network acts as the foundation for communities, applications, organisations and digital assets that is accessible for creation and utilization by anyone[1].
- Ethereum is renowned primarily for its native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH)[2].
- Ethereum was designed as the "upgrade" of Bitcoin, aiming to accomplish functionalities that Bitcoin couldn't achieve.
What can Ethereum do[1]?
- Banking: Ethereum offers an inclusive platform accessible to everyone, and it provides financial services such as lending, borrowing and savings products.
- An open internet: Users have full control over their own assets and identity, instead of them being controlled by a few mega-corporations.
- A peer-to-peer (p2p) network: Ethereum allows users to coordinate, make agreements or transfer digital assets directly with each other, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
- Censorship-resistant: No government or company has control over Ethereum. The decentralized nature of Ethereum makes it nearly impossible for anyone to ban its services.
- Commerce guarantees: Users benefit from a secure, built-in guarantee on Ethereum, assuring that funds will only change hands when agreed-upon conditions are met.
- Composable products: All applications are built on the same blockchain with a shared global state, meaning they can build off each other. This ensures that no one can remove essential tools or components relied upon, providing greater stability, trust, and user experience within the network.
Some popular applications built on the Ethereum blockchain are listed below:
| OpenSea | Largest NFT marketplace |
| Uniswap | Cryptocurrencies swapping platform |
| MetaMask | Most widely used crypto wallet |
| MakerDAO | Cryptocurrencies lending platform |
How does Ethereum work?
In brief, Ethereum = Blockchain + Smart contracts + ETH.
- Blockchain[4]
Blockchain is simply a database of specific data that continuously grows, with the following characteristics:
- Once data is stored in the database, it can never be modified or deleted. Each record on the blockchain is permanently preserved.
- No individual or organization can maintain the database alone. It requires the agreement of the majority of users within the database, with each user holding a copy of the database.
Imagine a network of 10 individuals. Each person has an empty folder and a blank page. Whenever any person performs an action, such as a transaction, a notification is sent to everyone in the network. Each person then records the notification on their own page. When the page is completely filled, each individual must seal the page's content and ensure that all pages in the network are identical. Once sealed, the content in the page can never be altered and the page is added to the folder.
Over time, these pages (blocks) containing content (transactions) will be sequentially added to the folders (chain), thus forming a database (blockchain).
- Smart contracts[5]
Smart contracts are computer programs stored on the Ethereum blockchain that allow converting conventional contracts into digital parallels. Smart contracts follows an "if this then that" structure, which means they behave exactly as programmed and cannot be altered. Contracts are essentially agreements. People make agreements verbally or write pen-and-paper contracts and fullfill the agreements after certain conditions are reached. However, these conventional contracts are not without their flaws. Enter smart contracts, the perfect solution to address these shortcomings.
| Conventional contracts | Smart contracts | |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Executed by human through the court system | Automatically executed |
| Validity | Valid only if both parties agree and sign | Can be vlidated by anyone on the Ethereum networks |
| Security | Less secure as they are stored in paper form or digitally | Highly secure as they are stored on a blockchain |
| Modification | Easily modified with mutual consent of both parties | Difficult to modify |
| Cost | Require the use of third-party intermediaries, making them more expensive | Cost-effective due to the removal of third-party intermediaries |
| Accuracy | Prone to errors due to human involvement | Accurate due to the use of code |
| Record Keeping | Records stored in paper form or digitally, not publicly available | Records stored on a blockchain and can be viewed publicly |
Smart contracts serve as the cornerstone of Ethereum applications. They have the capability to perform nearly anything that other computer programs can do with the above benefits. They can perform computations, create currency, store data, mint NFTs, send communications, generate graphics, etc.
- ETH
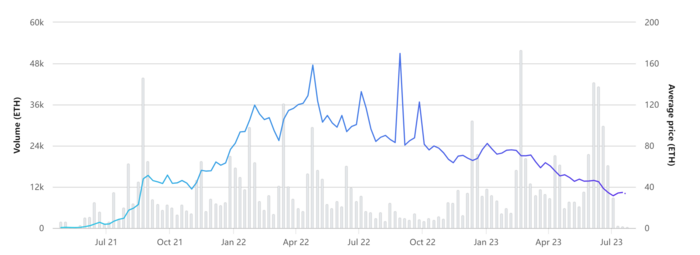
Every independent blockchain has its own native cryptocurrency that is used to reward miners and validators adding blocks to the blockchain and as a payment method, including for transaction fees (gas fees). In Ethereum's case, its native cryptocurrency is called Ether (ETH), which can be used to pay for executing smart contracts on the Ethereum platform. The price of ETH symbolizes the value of the Ethereum ecosystem, as Ethereum is not a company with stock[7]. Therefore, the primary method of investing in Ethereum is by purchasing ETH.
NFTs
NFTs, short for non-fungible tokens, represent ownership of unique itemsand enable the tokenisation of various assets, such as art, collectibles, and even real estate. Ownership of an asset is secured by blockchain. As mentioned before, no one can modify the record of ownership or copy/paste a new NFT into existence[8]. Although there are many blockchains supporting NFTs, such as Polygon, most NFT trade volume still resides on the Ethereum network[9].
The term non-fungible is used to describe things like a painting, a song file, or a photo. These things are not interchangeable for other items because they have unique properties. On the other hand, fungible items can be exchanged because their value defines them rather than their unique properties. For example, people can easily exchange a $10 bill for another $10, or 2 $5 bills[10].
Since the debut of the first NFT called "CryptoKitties" on the Ethereum blockchain back in 2017, NFTs have continuously surged in popularity over the years. NFTs sales can range anywhere from 15,000 to 50,000 in a week. This averages out to be an estimated $10 million to $20 million each week[11]. The famous "Bored Ape Yacht Club" NFT was initially released at a price of 0.08 ETH, which was approximately $190 at the time. It reaches its peak in 2022, surpassing 160 ETH. Even at present (July 2023), it remains actively traded daily and maintainces an impressive floor price of 30 ETH, which equates to roughly $55,000.
NFTs hold immense potential within the metaverse, enabling users to securely own and trade virtual assets. With the metaverse attracting attention from major corporations like Facebook, now known as Meta, there is no doubt that NFTs will experience a surge in popularity.[12].
The success of NFTs is a testament to the power of Ethereum, showcasing its capabilities and potential. However, it's essential to recognize that NFTs are just one of the numerous applications that Ethereum supports.
Ethereum vs. Bitcoin
| Ethereum[15] | Bitcoin[16] | |
|---|---|---|
| Popularity | #2 | #1 |
| Rating | 4.4 | 4.5 |
| Type | Decentralized blockchain | Digital currency |
| Circulating supply | 120.2M ETH | 19.4M BTC |
| Total supply | Infinite | 21M BTC |
| Market cap | $222.4B | $568.1B |
| All time high | $4,891.70 | $68,789.63 |
| Mining method | Proof of Stake (PoS) | Proof of Work (PoW) |
- Since Bitcoin stands as the pioneering and most renowned cryptocurrency, drawing a comparison between Bitcoin and Ethereum proves highly beneficial when analyzing Ethereum. As Bitcoin's primary competitor, ETH is ranked #2 on most cryptocurrency platforms, while Bitcoin is ranked #1.
- While this section focuses on comparing Ethereum and Bitcoin, it's essential to acknowledge that they are not of the same kind. Ethereum operates as a decentralized blockchain, where cryptocurrency is merely one of its numerous applications (financial services, games, social networks, etc.). In contrast, Bitcoin exclusively functions as a cryptocurrency, akin to the virtual counterpart of a dollar.
- The circulating supply of a cryptocurrency represents the number of tokens that have been issued and are actively available in the market. For Bitcoin, over 90% of its total supply has already been mined. On the other hand, ETH has an infinite supply.
- While the concept of unlimited supply may raise concerns for ETH, it actually contributes to its stability as a cryptocurrency. This characteristic prevents scarcity-driven market behaviours and allows for a more sustainable and adaptable ecosystem for Ethereum, ensuring its continued relevance and functionality.
- Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, envisioned the creation of Ethereum with the goal of harnessing blockchain technology and extend its applications far beyond just being a digital currency like Bitcoin.[17].
- Ethereum uses the PoS mining method wherein miners' scores are determined by the amount of tokens in their digital wallets and the duration they have held them. The miner with the highest stake has a better chance of being selected to validate a transaction and receive a reward[18]. Bitcoin uses the PoW mining method, where miners are rewarded for the computational work they perform[19].
Valuation
The total value of all cryptocurrencies is $1.23 trillion, in July 2023[20]. At the same time, ETH has a total value of $222.4 billion[15], which is approximately 18% of the market. In the near future, this percentage will continuously increase because ETH has an infinite supply, while Bitcoin is approaching its total supply limit.
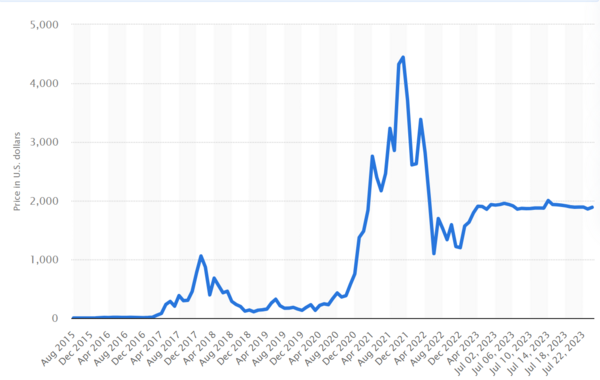
The initial release price of ETH is $0.31 per token in 2015, and it was under $1 for the major part of 2015. But by March 2016 Ether crossed the $10 mark. By 2017, ETH had gained popularity and reached $100 in May 2017. By the end of 2017, ETH had reached a value of $774.69 and within the first week of 2018, it crossed the $1000 mark. After the cryptocurrency crash in 2018, ETH was reduced to under just $100. From 2019 to 2021, ETH once again continued to rally and reached its highest price of $4,815 on November 9, 2021. During the first half of 2022, ETH's price experienced a significant drop, but since then, it has been consistently hovering around $2000 up until the current date in July 2023[21].
Risks
- Volatility: The value of ETH can experience rapid and substantial fluctuations as shown in the previous section, leading to potential losses for investors and users.
- Regulatory: ETH subject to regulatory scrutiny in various jurisdictions. Changes in government regulations or policies can impact the adoption, usage, and value of Ethereum[23].
- Collapsing of Bitcoin: Bitcoin remains the leading cryptocurrency, valued highly for its position in the market, but it lacks versatility beyond its use as a digital currency. The potential for a collapse of Bitcoin is a real concern, and such an event could have a significant impact on all other cryptocurrencies, including ETH. A similar situation occurred in 2018 when the market experienced a downturn.
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 https://ethereum.org/en/what-is-ethereum/
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/ethereum.asp
- ↑ https://www.makeuseof.com/best-dapps-ethereum-eth/
- ↑ https://online.stanford.edu/how-does-blockchain-work
- ↑ https://ethereum.org/en/smart-contracts/
- ↑ https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/smart-contracts-vs-traditional-contracts/
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/what-are-native-tokens-6754173
- ↑ https://ethereum.org/en/nft/#what-are-nfts
- ↑ https://nftnow.com/guides/ethereum-and-nfts-a-comprehensive-guide-for-beginners-and-experts/
- ↑ https://www.binance.com/en/nft/what-is-nft
- ↑ https://www.web3.university/tracks/build-your-first-nft/brief-history-of-nfts
- ↑ https://www.fintechnews.org/the-relationship-between-nfts-and-the-metaverse/
- ↑ https://www.statista.com/outlook/dmo/fintech/digital-assets/nft/worldwide#users
- ↑ https://opensea.io/collection/boredapeyachtclub/activity
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 https://www.coinbase.com/price/ethereum
- ↑ https://www.coinbase.com/price/bitcoin
- ↑ https://time.com/6158182/vitalik-buterin-ethereum-profile/
- ↑ https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/what-is-proof-of-stake
- ↑ https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/proof-work.asp
- ↑ https://www.coingecko.com/en/global-charts
- ↑ https://www.globaldata.com/data-insights/financial-services/ethereums-price-history/
- ↑ https://www.statista.com/statistics/806453/price-of-ethereum/
- ↑ https://www.axios.com/2022/07/27/regulatory-risk-ethereum-security-model-proof-of-stake-sec