Phuc Labs: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "'''Digitally recovering resources from waste, making ecological vitality profitable''' == Summary == * Co-founder’s prior VC-funded startup sold to Uber for $1.1B * Patented AI & robotics tech sorts & recycles precious metals from e-waste * Novel digital tech produces 30% more efficient using 80% less energy * Large market opportunity with e-waste worth $65B * Pilots w/ largest battery maker in U.S. & e-waste recycler in Philippines * Veteran start-up team w/ proven...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Digitally recovering resources from waste, making ecological vitality profitable''' | '''Digitally recovering resources from waste, making ecological vitality profitable''' | ||
[[File:Phuclabslogo.png|thumb|200x200px]] | |||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
== Problem == | == Problem == | ||
== The world’s essential metals are trapped in e-waste streams == | === The world’s essential metals are trapped in e-waste streams === | ||
The global economy depends on critical resources like copper, palladium, and gold for everything from EV batteries to circuit boards. Most of these resources are now trapped within global e-waste streams of discarded phones, computers, and electronics—and worth an estimated $57B. | '''The global economy depends on critical resources like copper, palladium, and gold''' for everything from EV batteries to circuit boards. Most of these resources are now trapped within global e-waste streams of discarded phones, computers, and electronics—and worth an estimated $57B. | ||
Current demand for these metals is met by increasing mining operations, and mining new material outpaces recycling the old. In fact, the recycling rate for e-waste is estimated to be less than 20%. But both virgin mining and current recovery methods are unsustainable: they’re energy-intensive, inefficient, and a massive source of CO2 emissions. | Current demand for these metals is met by increasing mining operations, and mining new material outpaces recycling the old. In fact, '''the recycling rate for e-waste is estimated to be less than 20%'''. But both virgin mining and '''current recovery methods are unsustainable''': they’re energy-intensive, inefficient, and a massive source of CO2 emissions. | ||
Meantime, global reserves of these precious resources grow scarce. | Meantime, global reserves of these precious resources grow scarce. | ||
[[File:36c64775b1a12ab7bc81c1ea506ee8616a8fdc9.png]] | |||
== Solution == | == Solution == | ||
== Profitable & sustainable rare metal recycling == | === Profitable & sustainable rare metal recycling === | ||
Why mine for virgin metals when they can be recovered and recycled from the ever-growing stream of global electronic waste? | '''Why mine for virgin metals when they can be recovered and recycled''' from the ever-growing stream of global electronic waste? | ||
Phuc Labs has modernized recycling technology for e-waste and valuable earth metals to make ecological vitality profitable. Rather than relying on traditional analog methods like filtration technology or smelting—both of which are highly inefficient and polluting—our solution is a digital innovation: | Phuc Labs has '''modernized recycling technology for e-waste and valuable earth metals''' to make ecological vitality profitable. Rather than relying on traditional analog methods like filtration technology or smelting—both of which are highly inefficient and polluting—our solution is a digital innovation: | ||
We use computer vision and robotics to identify and recover resources from waste with higher accuracy and less energy, thus relieving pressure on the global supply chain and empowering manufacturing and industrial companies to meet sustainable development goals. | We use computer vision and robotics to '''identify and recover resources from waste with higher accuracy and less energy''', thus relieving pressure on the global supply chain and '''empowering manufacturing and industrial companies to meet sustainable development goals.''' | ||
[[File:279320420b083e4f99626f1fe9eeb6e031667838.png]] | |||
== Product == | == Product == | ||
== High-purity resource recovery, powered by AI & robotics == | === High-purity resource recovery, powered by AI & robotics === | ||
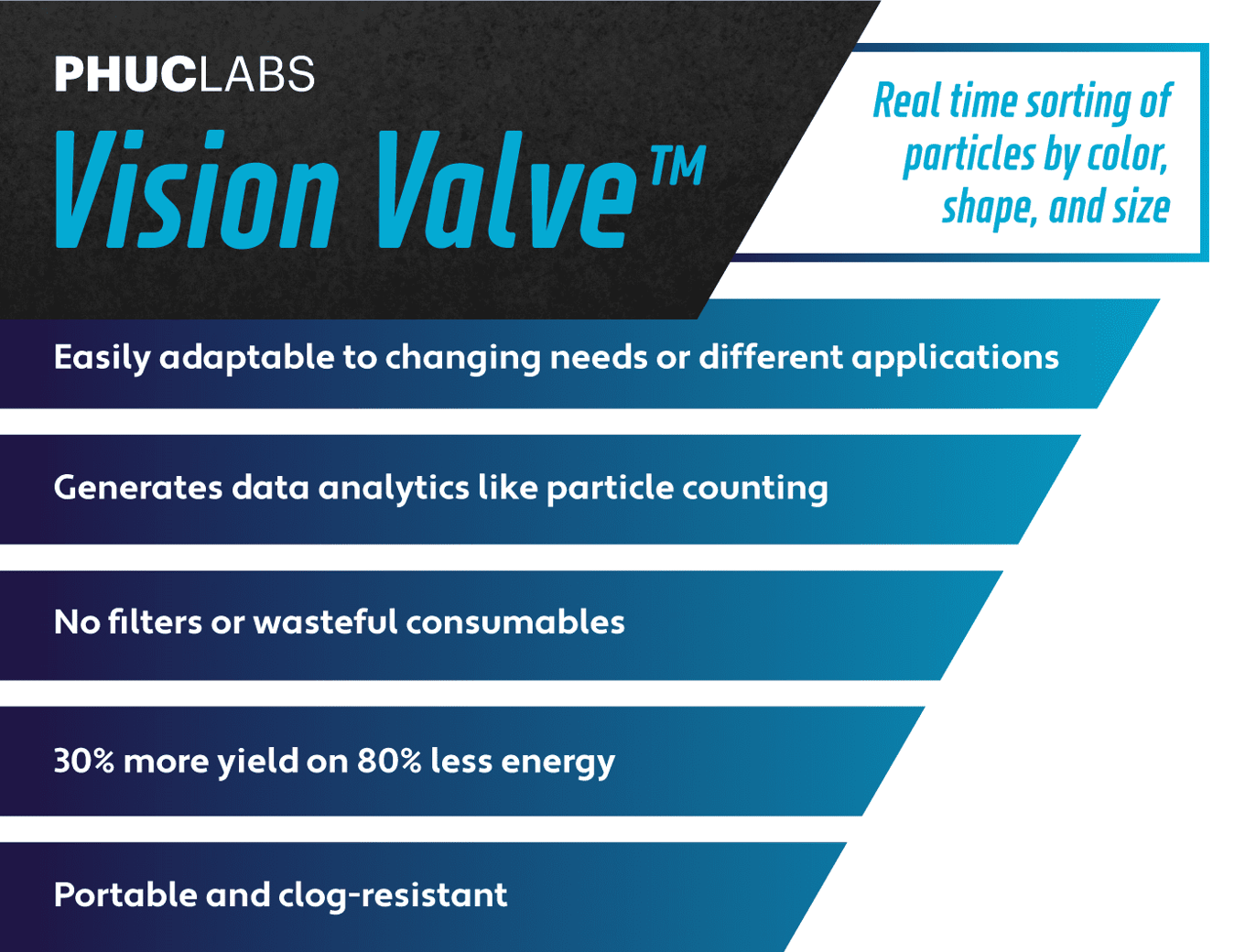
Vision Valve™ is Phuc Labs’ proprietary mineral and resource recovery technology for unprecedented efficiency in reclaiming critical resources from e-waste. | Vision Valve™ is Phuc Labs’ proprietary mineral and resource recovery technology for '''unprecedented efficiency in reclaiming critical resources from e-waste.''' | ||
=== How it works: === | |||
# After e-waste is broken down and mixed into carrier fluid that flows through the Vision Valve™ system, the software analyzes the stream, identifies and sorts resource particles, then physically directs them via robotic valves to the correct output tank. | # After e-waste is broken down and mixed into carrier fluid that flows through the Vision Valve™ system, the software analyzes the stream, identifies and sorts resource particles, then physically directs them via robotic valves to the correct output tank. | ||
# The salvaged particles of critical resources like copper and gold are filtered with enough purity to be immediately redirected and sold back into the supply chain. | # The salvaged particles of critical resources like copper and gold are filtered with enough purity to be immediately redirected and sold back into the supply chain. | ||
[[File:9cc468720095f1cfb51a223f2c9f20378f19cf7.png]] | |||
== Traction == | == Traction == | ||
== Global reach & joint partnerships == | === Global reach & joint partnerships === | ||
Phuc Labs’ patented Vision Valve technology is tested and proven with successful pilot projects, and we’ve signed agreements and Letters of Intent with leading industry partners, including: | Phuc Labs’ patented Vision Valve technology is '''tested and proven''' with '''successful pilot projects''', and '''we’ve signed agreements and Letters of Intent with leading industry partners''', including: | ||
# Joint venture with Enviscicle, for industrial waste recovery and remediation such as IRI, the largest e-waste recycler in the Philippines | # Joint venture with Enviscicle, for industrial waste recovery and remediation such as IRI, the largest e-waste recycler in the Philippines | ||
# Active pilot with Retriev, North America's largest and oldest battery recycler. | # Active pilot with Retriev, North America's largest and oldest battery recycler. | ||
# Anglo-American, a publicly-traded Top 5 global mining company for reclamation of critical minerals. | # Anglo-American, a publicly-traded Top 5 global mining company for reclamation of critical minerals. | ||
[[File:97748025efd2e2eff3b083491e0dd339307634c.png]] | |||
== Customers == | |||
== | === LOIs with major sector leaders === | ||
Phuc Labs’ '''customer pipeline includes''' deployment of our Vision Valve tech with '''large e-waste companies''' focused on '''reclaiming copper, critical metals, and precious minerals.''' | |||
Beyond e-waste, the cross-industry application of our tech is vast. Because Vision Valve operates using fluid, it '''can be rapidly deployed to wastewater treatment, mining, food & beverage processing operations''' to immediately reclaim profitable resources from these diverse waste streams. | |||
[[File:4269c78c046663304579a6f628d0c613acfdc275.png]] | |||
== Business model == | == Business model == | ||
== A profitable link in the e-waste recycling chain == | === A profitable link in the e-waste recycling chain === | ||
Phuc Labs’ technology is easily deployable for a range of use cases and industries, and our business model has diverse established and potential revenue streams. We generate revenue by selling the metals we recover and sort, and by meeting our customers’ unique waste separation needs domestically and through strategic joint ventures abroad. | Phuc Labs’ technology is easily deployable for a range of use cases and industries, and our business model has diverse established and potential revenue streams. We generate revenue by selling the metals we recover and sort, and by meeting our customers’ unique waste separation needs domestically and through strategic joint ventures abroad. | ||
Phuc Labs is now extracting palladium, gold, copper, silver, and lithium, at an expected annual revenue of over $1M with the largest e-waste recycler in the Philippines. | Phuc Labs is now extracting palladium, gold, copper, silver, and lithium, at an expected '''annual revenue of over $1M with the largest e-waste recycler in the Philippines.''' | ||
[[File:9b9ce90d090c9d9c3d7522d4f515d23f6747b64.png]] | |||
== Market == | == Market == | ||
== Rare earth metals demand to triple by 2030 == | === Rare earth metals demand to triple by 2030 === | ||
Phuc Labs’ proprietary Vision Valve technology serves a total addressable e-waste market worth $65 billion. | Phuc Labs’ proprietary Vision Valve technology serves a '''total addressable e-waste market worth $65 billion.''' | ||
As global industry adapts to meet low and zero-carbon emissions standards, our ultra-efficient Vision Valve stands to benefit significantly from companies seeking solutions to increase profit while reducing their carbon footprint. | As global industry adapts to meet low and zero-carbon emissions standards, our ultra-efficient Vision Valve stands to benefit significantly from '''companies seeking solutions to increase profit while reducing their carbon footprint.''' | ||
[[File:6b81b1d236348251349f451f211e750c879ea6ae.png]] | |||
== Competition == | == Competition == | ||
== The only resource recovery using digitized separation == | === The only resource recovery using digitized separation === | ||
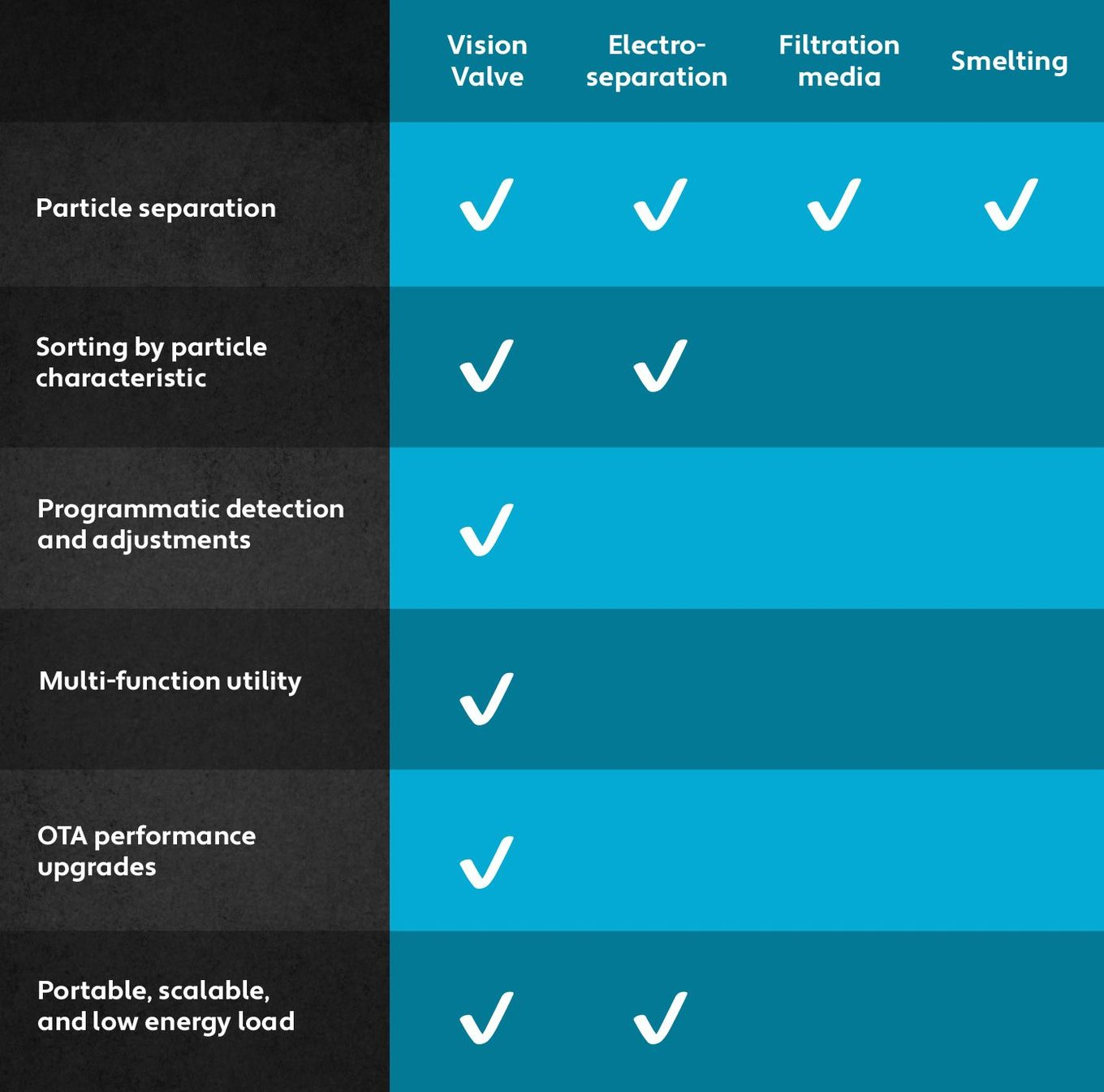
Phuc Labs’ competitors are the companies using outdated, inefficient smelting and filtration technology. | Phuc Labs’ competitors are the companies using outdated, inefficient smelting and filtration technology. | ||
Our unique and patented technology is a high barrier to entry for would-be direct competitors: no other company can develop the combination of machine learning AI plus fast-actuating valves for e-waste recovery. | Our unique and '''patented technology''' is a high barrier to entry for would-be direct competitors: '''no other company can develop the combination of machine learning AI plus fast-actuating valves for e-waste recovery.''' | ||
Vision Valve recovers and sorts multiple particles that conventional technologies cannot—all while being cost-efficient, energy-efficient, low maintenance, portable, and easily scalable. Because the core technology is digital and uses ML/AI, Vision Valve's performance improves over time with more data. | Vision Valve recovers and sorts multiple particles that conventional technologies cannot—all while being cost-efficient, energy-efficient, low maintenance, portable, and easily scalable. Because the core technology is digital and uses ML/AI, Vision Valve's performance improves over time with more data. | ||
[[File:6d16f1c8f8856f0b06e60ee07556fc6d6c56c92.png]] | |||
== Vision and strategy == | == Vision and strategy == | ||
== Scaling internationally with $1M+ in revenue == | === Scaling internationally with $1M+ in revenue === | ||
As we continue to scale our customer pipeline, we’re also expanding our team and IP portfolio to drive momentum and innovation towards dominating this niche. | As we continue to '''scale our customer pipeline, we’re also expanding our team and IP portfolio''' to drive momentum and innovation towards dominating this niche. | ||
[[File:55cdd396baad3cbdd83d1888fb9e3ba291b67e3.png]] | |||
== Funding == | == Funding == | ||
== $1.3M raised from leading VCs == | === $1.3M raised from leading VCs === | ||
Phuc Labs’ transformative technology has received investment from several funds focused on climate-innovative companies. | Phuc Labs’ transformative technology has received investment from several funds focused on '''climate-innovative companies.''' | ||
We’ve raised $1.3M from investors including MCJ Collective, Climate Capital, AI Sprout, and founding partner of Spark Capital, Bijan Sabet. | We’ve '''raised $1.3M from investors''' including MCJ Collective, Climate Capital, AI Sprout, and founding partner of Spark Capital, Bijan Sabet. | ||
== Founders == | == Founders == | ||
== Previous startups include $1.1 billion exit to Uber == | === Previous startups include $1.1 billion exit to Uber === | ||
CEO Phuc Vinh Truong has dedicated his career to creating cutting-edge, transformative technologies. He started 3 companies that have received over $25 million of VC funding, and has led the development of complex enterprise-grade systems which serviced millions of users. | CEO Phuc Vinh Truong has dedicated his career to creating cutting-edge, transformative technologies. He '''started 3 companies that have received over $25 million of VC funding''', and has '''led the development of complex enterprise-grade systems''' which serviced millions of users. | ||
Head of Business Phuc Thien Truong brings 20+ years of startup experience as a 4x co-founder. He’s created revenue streams worth up to $6 million, and managed 4 exits as founder and C-Suite member, including one to Uber for $1.1 billion. | Head of Business Phuc Thien Truong brings '''20+ years of startup experience as a 4x co-founder'''. He’s created '''revenue streams worth up to $6 million,''' and managed '''4 exits as founder and C-Suite member, including one to Uber for $1.1 billion.''' | ||
[[File:F81625b28b298203b2f9163759c24df3db4be2c4.png]] | |||
== Phuc Labs Team == | == Phuc Labs Team == | ||
| Line 130: | Line 144: | ||
Expert in 3D printing: researching, inventing, designing, fabricating, & testing solutions for 3D printing with metal powder at high speed. Mechanical Engineering at UMass Amherst, 2004. | Expert in 3D printing: researching, inventing, designing, fabricating, & testing solutions for 3D printing with metal powder at high speed. Mechanical Engineering at UMass Amherst, 2004. | ||
[[Category:Thesis]] | |||
[[Category:Equities]] | |||
__INDEX__ | |||
Latest revision as of 14:26, 20 August 2022
Digitally recovering resources from waste, making ecological vitality profitable
SummaryEdit
- Co-founder’s prior VC-funded startup sold to Uber for $1.1B
- Patented AI & robotics tech sorts & recycles precious metals from e-waste
- Novel digital tech produces 30% more efficient using 80% less energy
- Large market opportunity with e-waste worth $65B
- Pilots w/ largest battery maker in U.S. & e-waste recycler in Philippines
- Veteran start-up team w/ proven value creation & multiple successful exits
ProblemEdit
The world’s essential metals are trapped in e-waste streamsEdit
The global economy depends on critical resources like copper, palladium, and gold for everything from EV batteries to circuit boards. Most of these resources are now trapped within global e-waste streams of discarded phones, computers, and electronics—and worth an estimated $57B.
Current demand for these metals is met by increasing mining operations, and mining new material outpaces recycling the old. In fact, the recycling rate for e-waste is estimated to be less than 20%. But both virgin mining and current recovery methods are unsustainable: they’re energy-intensive, inefficient, and a massive source of CO2 emissions.
Meantime, global reserves of these precious resources grow scarce.
SolutionEdit
Profitable & sustainable rare metal recyclingEdit
Why mine for virgin metals when they can be recovered and recycled from the ever-growing stream of global electronic waste?
Phuc Labs has modernized recycling technology for e-waste and valuable earth metals to make ecological vitality profitable. Rather than relying on traditional analog methods like filtration technology or smelting—both of which are highly inefficient and polluting—our solution is a digital innovation:
We use computer vision and robotics to identify and recover resources from waste with higher accuracy and less energy, thus relieving pressure on the global supply chain and empowering manufacturing and industrial companies to meet sustainable development goals.
ProductEdit
High-purity resource recovery, powered by AI & roboticsEdit
Vision Valve™ is Phuc Labs’ proprietary mineral and resource recovery technology for unprecedented efficiency in reclaiming critical resources from e-waste.
How it works:Edit
- After e-waste is broken down and mixed into carrier fluid that flows through the Vision Valve™ system, the software analyzes the stream, identifies and sorts resource particles, then physically directs them via robotic valves to the correct output tank.
- The salvaged particles of critical resources like copper and gold are filtered with enough purity to be immediately redirected and sold back into the supply chain.
TractionEdit
Global reach & joint partnershipsEdit
Phuc Labs’ patented Vision Valve technology is tested and proven with successful pilot projects, and we’ve signed agreements and Letters of Intent with leading industry partners, including:
- Joint venture with Enviscicle, for industrial waste recovery and remediation such as IRI, the largest e-waste recycler in the Philippines
- Active pilot with Retriev, North America's largest and oldest battery recycler.
- Anglo-American, a publicly-traded Top 5 global mining company for reclamation of critical minerals.
CustomersEdit
LOIs with major sector leadersEdit
Phuc Labs’ customer pipeline includes deployment of our Vision Valve tech with large e-waste companies focused on reclaiming copper, critical metals, and precious minerals.
Beyond e-waste, the cross-industry application of our tech is vast. Because Vision Valve operates using fluid, it can be rapidly deployed to wastewater treatment, mining, food & beverage processing operations to immediately reclaim profitable resources from these diverse waste streams.
Business modelEdit
A profitable link in the e-waste recycling chainEdit
Phuc Labs’ technology is easily deployable for a range of use cases and industries, and our business model has diverse established and potential revenue streams. We generate revenue by selling the metals we recover and sort, and by meeting our customers’ unique waste separation needs domestically and through strategic joint ventures abroad.
Phuc Labs is now extracting palladium, gold, copper, silver, and lithium, at an expected annual revenue of over $1M with the largest e-waste recycler in the Philippines.
MarketEdit
Rare earth metals demand to triple by 2030Edit
Phuc Labs’ proprietary Vision Valve technology serves a total addressable e-waste market worth $65 billion.
As global industry adapts to meet low and zero-carbon emissions standards, our ultra-efficient Vision Valve stands to benefit significantly from companies seeking solutions to increase profit while reducing their carbon footprint.
CompetitionEdit
The only resource recovery using digitized separationEdit
Phuc Labs’ competitors are the companies using outdated, inefficient smelting and filtration technology.
Our unique and patented technology is a high barrier to entry for would-be direct competitors: no other company can develop the combination of machine learning AI plus fast-actuating valves for e-waste recovery.
Vision Valve recovers and sorts multiple particles that conventional technologies cannot—all while being cost-efficient, energy-efficient, low maintenance, portable, and easily scalable. Because the core technology is digital and uses ML/AI, Vision Valve's performance improves over time with more data.
Vision and strategyEdit
Scaling internationally with $1M+ in revenueEdit
As we continue to scale our customer pipeline, we’re also expanding our team and IP portfolio to drive momentum and innovation towards dominating this niche.
FundingEdit
$1.3M raised from leading VCsEdit
Phuc Labs’ transformative technology has received investment from several funds focused on climate-innovative companies.
We’ve raised $1.3M from investors including MCJ Collective, Climate Capital, AI Sprout, and founding partner of Spark Capital, Bijan Sabet.
FoundersEdit
Previous startups include $1.1 billion exit to UberEdit
CEO Phuc Vinh Truong has dedicated his career to creating cutting-edge, transformative technologies. He started 3 companies that have received over $25 million of VC funding, and has led the development of complex enterprise-grade systems which serviced millions of users.
Head of Business Phuc Thien Truong brings 20+ years of startup experience as a 4x co-founder. He’s created revenue streams worth up to $6 million, and managed 4 exits as founder and C-Suite member, including one to Uber for $1.1 billion.
Phuc Labs TeamEdit
Dr. Richard Fontana
Chief Technology Officer (CTO)
40+ years as a mechanical engineer w/ government projects & startups: Kiva Systems (acq. by Amazon Robotics) & Desktop Metal (IPO). Expertise in R&D, program management, & tech to market. Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering, MIT.
Dr. Varada Palakkal
Director of Chemical Engineering
Research expertise in materials & technology development for electrochemical separation & energy conversion. Patented 5x published work at Argonne National Laboratories. Postdoc at UT Austin. PhD at Louisiana State University.
Matthew Schwab
Director of Engineering
Experienced engineer with startup and management experience at Oculus (Haptics), Offworld (Autonomous Mining), and General Dynamics (MBSE), and civil engineering in the U.S. Air Force. M.Sc. in Mechanical Engineering from CSULA.
Aaron Kessler
Business Development
20+ years experience as an entrepreneur across 8 startups, managing client support, sales, marketing, business operations, and human resources. B.S. History from Harvard University, 1998.
Midnight Zero
VP Mechanical Engineering
Expert in 3D printing: researching, inventing, designing, fabricating, & testing solutions for 3D printing with metal powder at high speed. Mechanical Engineering at UMass Amherst, 2004.