Sony Group Corporation
 | |
 Sony's Headquarters Complex at Sony City in Minato, Tokyo | |
Native name | ソニーグループ株式会社 |
|---|---|
Romanized name | Sonī Gurūpu kabushiki kaisha |
| Formerly |
|
| Type | Public |
| Industry | Conglomerate |
| Founded | 7 May 1946 Nihonbashi, Chūō, Tokyo, Japan[2] |
| Founders | |
| Headquarters | Sony City, , Japan |
Area served | Worldwide |
Key people |
|
| Products | |
| Services | |
| Revenue | |
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
Number of employees | 113,000[3] (2023) |
| Divisions |
|
| Subsidiaries | See list of subsidiaries |
| Website | |
| Footnotes / references Financials as of fiscal year ended 31 March 2021[update]. References:[5][6] | |
Sony Group Corporation, commonly stylized as SONY in capital letters, is a significant Japanese multinational conglomerate with its headquarters located in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Sony, a multinational corporation established in 1946, has established itself as a prominent global leader across diverse industries, boasting a significant and enduring heritage. Sony, a prominent global entity, possesses an extensive assortment of consumer and professional electronic devices, thereby solidifying its position as one of the largest producers on a global scale. The corporation's sphere of influence encompasses several sectors such as technology, gaming, entertainment, and media, rendering it a comprehensive and influential entity.
Sony has exceptional proficiency in various fields, establishing itself as a prominent force in the field of technology. With a substantial market share of 55 percent, this company has established itself as the leading maker of image sensors on a global scale. Moreover, Sony is recognized as the second-largest manufacturer of cameras and occupies a prominent position among the leaders in semiconductor sales. Significantly, it maintains a dominant position in the high-end television market segment, specifically for televisions with screen sizes exceeding 55 inches and a price point surpassing $2,500. Additionally, it asserts its position as the second-largest television brand in terms of market share and holds the third position worldwide in terms of yearly sales statistics among television manufacturers.
Sony Group Corporation operates as the parent company for a diverse range of companies within the Sony Group conglomerate. The conglomerate comprises various significant businesses, including Sony Corporation, Sony Semiconductor Solutions, Sony Entertainment (consisting of Sony Pictures and Sony Music), Sony Interactive Entertainment, Sony Financial Group, Sony Creative Products, and additional subsidiaries. The complex network established by Sony facilitates the provision of a wide range of products and services, encompassing several sectors such as electronics, entertainment, gaming, and finance.
The branding of the corporation is characterized by the motto "We are Sony," which signifies the company's dedication to innovation, excellence, and influence. Throughout its history, Sony has embraced a range of slogans, including "The One and Only," "It's a Sony," and most recently "Be Moved." The aforementioned slogans reflect Sony's progression and its endeavor to generate a significant influence in the lives of global consumers.
Sony's corporate affiliations encompass the Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group (SMFG) corporate conglomerate, so highlighting its prominent standing within Japan's convoluted business milieu. The company is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and also has a secondary listing on the New York Stock Exchange through American depositary receipts. The inclusion of this entity in the esteemed Fortune Global 500 list serves as a testament to its notable position within the global business landscape.
Operations edit edit source
What is the company mission? edit edit source
Sony is a company that wishes to inspire and fulfil ones curiosity. They want to use their unlimited passion for technology, content and services to deliver groundbreaking new excitement and entertainment
What are the main offerings of the company? edit edit source
| Products | comments |
|---|---|
| Televisions | Sony released the TV8-301, the world's first all-transistor television in 1959. Sony introduced 'BRAVIA' , the company's in-house brand producing high-definition LCD television, projection TVs and front projectors. In November 2007, Sony released the first OLED television and in 2013 the first 4K OLED one. As of 2012, Sony was the third largest maker of televisions in the world. |
| Playstation | playstation is Sony's video gaming brand consisting of home and handheld video game consoles. The first Playstation was released in December 1994, with the most recent 'Playstation 5' being released in November 2020. The Playstation 5 sold 10 million units in its first 249 days, making it the fastest-selling Playstation console to-date. The Playstation Network is an online service with about 110 million registered users. It consists of an online virtual market called the 'Playstation Store' and a subscription service known as 'Playstation Plus'. |
| Smartphones | 'Sony Experia' is the smartphone range from Sony operating on an Android based system. The X10 was released at the start of 2010, the first phone with an android system. The Z series smartphones were then introduced with an omni-balance design and water resistance. The Experia Z is the earliest known device to feature high dynamic range filming at 1080p. The 'Sony Experia 1 V' was released in May of 2023 and includes a 4K OLED display. |
| Audio services | Sony offer a wide range of audio products including speakers, headphones, earbuds, audio systems, sound bars and digital voice recorders. Sony released a new range of wireless headphones with noise cancellation features with the newest model named the 'WH-CH720N' being released in Spring 2023. Sony have a range of portable and battery built speakers with the 'SRS-XV800' part speaker being released earlier in 2023. |
| Cameras | Sony offers a wide range of digital cameras, action cameras and camcorders. In 2010, Sony released their first mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras which were the NEX-3 and the NEX-5. 'Sony alpha' was introduced in 2006 consisting of the digital and mirrorless cameras. The 'Sony a9 mark 3 lll' is a full frame mirrorless camera which is expected to be released in late 2023. |
| Cloud services | In September 2022 Sony launched its cloud production platform which includes online creative collaboration and content management service. The cloud platform includes: A content transfer application from camera to cloud; Cloud storage; Master Cut (an online video pre editing service). Sony promises to create smarter workflows across production, post-production and delivery. The platform is supported by AI and machine learning enabling full creativity. |
| Media Storage and Cables | Sony also have a range of media storage devices such as memory cards, USB flash drives and External HDD-SSD. Sony was the first company to bring CFexpress Type A cards with a record breaking 1920GB entry in it's Type a lineup. |
Business Model[7] edit edit source
Sony Corporation, a Japanese multinational conglomerate, excels in Consumer Electronics, Gaming, Entertainment, and Financial Services. Using the business model canvas, we see its success factors:
Value Propositions: Sony delivers top-notch consumer electronics, gaming consoles, movies, and music. Innovation, tech prowess, and diversification bolster its brand and customer loyalty.
Customer Segments: Sony's products cater to individuals, gamers, businesses, and industries. Its broad client base spans demographics and needs.
Channels: Sony uses online/offline platforms, like its official store, third-party online sellers, physical retail, and global retail partnerships.
Customer Relationships: Sony's strong brand and reputation cultivate trust. Social media, loyalty programs, support, and warranties further customer connections.
Key Resources: Sony relies on advanced tech, R&D, IP, and global partnerships. Skilled workforce also drives its success.
Key Activities: Sony focuses on R&D, manufacturing, marketing, and distribution to stay competitive in diverse sectors.
Key Partnerships: Suppliers, distributors, retailers, and entertainment collaborators form Sony's network. Strategic partnerships drive success in divisions.
Cost Structure: Sony's costs encompass manufacturing, R&D, marketing, distribution, etc. Its diversified revenue streams include electronics sales, gaming subscriptions, and entertainment profits.
In essence, Sony thrives through diverse products, broad customer outreach, and varied distribution channels. Innovation, tech leadership, and strategic partnerships fuel its competitive edge and success.
Past Mergers and Acquisitions Deals edit edit source
Columbia Pictures Entertainment, Inc. (1989): One of Sony's most significant acquisitions was its purchase of Columbia Pictures. This move allowed Sony to establish itself as a major player in the entertainment industry by gaining access to a large library of films and television shows.
Sony Ericsson (2001-2012): Sony entered a joint venture with Ericsson to create Sony Ericsson, a mobile phone manufacturing company. Sony later acquired Ericsson's share of the venture, fully integrating it into its own operations, and renaming it Sony Mobile Communications.
CBS Records (1988): Sony acquired CBS Records, which was later renamed Sony Music Entertainment, giving the company a strong presence in the music industry.
Sony BMG Music Entertainment (2004-2008): Sony acquired the Bertelsmann Music Group's (BMG) 50% stake in Sony BMG, making it a wholly-owned subsidiary. However, this was followed by regulatory concerns, leading to the divestiture of the joint venture, resulting in Sony Music Entertainment.
ATV Music Publishing (1995): Sony formed a joint venture with Michael Jackson to acquire the ATV catalog, which included the rights to numerous iconic songs, including many of The Beatles' works. In 2016, Sony acquired Jackson's stake in the joint venture, gaining full control of ATV Music Publishing.
Epic Records (1988): As part of the acquisition of CBS Records, Sony gained ownership of Epic Records, a major record label known for its roster of popular artists.
Insomniac Games (2019): Sony acquired Insomniac Games, a well-known video game developer responsible for creating franchises like "Ratchet & Clank" and "Spider-Man."
Crunchyroll (Pending as of 2021): Sony announced its intention to acquire Crunchyroll, a popular streaming service focused on anime content. This acquisition aimed to bolster Sony's presence in the streaming industry, particularly in the anime genre.
Management Team edit edit source
Chairman and CEO edit edit source

President, COO and CFO edit edit source

Executive Deputy President and CSO edit edit source

Senior Executive Vice President and CTO edit edit source

Executive Vice President, CDO and CIO edit edit source

Market edit edit source
Market Overview
Sony Corporation is an international corporation that operates within the technology and entertainment sector, whose commercial operations involve an extensive range of products and services, spanning consumer electronics, gaming, music, film, and various other areas. The industry is propelled by key factors like as technical innovation, digitisation, and convergence, as organisations effort to establish cohesive experiences across several platforms. Sony, being a significant entity in the industry, strategically utilises its research and development capabilities to introduce innovative goods that are at the forefront of technological advancements. These items include the highly popular PlayStation game console, top-notch audiovisual equipment, and advanced professional cameras. The gaming industry, driven by immersive experiences, internet connectivity, and e-sports, has emerged as a significant source of revenue. Moreover, the escalating need for content streaming and digital entertainment has resulted in the augmentation of Sony's media creation and distribution efforts. Furthermore, the increasing importance of sustainability and ethical issues has led firms such as Sony to prioritise eco-friendly methods and social responsibility. In light of the obstacles presented by upheavals in the global supply chain and fierce competition, Sony's strategic efforts are in accordance with prevailing trends in the industry. The company aims to foster innovation, diversify its offerings, and effectively connect with a consumer base that is both dynamic and technologically proficient.
Competitive Landscape
The commercial environment in which Sony Corporation operates is characterised by a dynamic interaction between well-established industry leaders and new participants, all competing for market dominance across different segments of the technology and entertainment sector. Within the domain of consumer electronics, Sony encounters formidable competition from corporations such as Samsung and LG, who present a diverse range of products spanning from smartphones to household appliances. Furthermore, within the gaming industry, Sony's PlayStation platform competes with Microsoft's Xbox and Nintendo's gaming consoles, resulting in an ongoing cycle of innovation and the provision of exclusive content in order to attract and retain gamers. The realm of streaming and entertainment is characterised by fierce competition from prominent digital entities such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+, alongside music streaming platforms like Spotify and Apple Music. In order to remain competitive, Sony must consistently allocate resources towards research and development efforts to produce novel goods that align with the changing interests of consumers. Sony has utilized strategic alliances, collaborations, and acquisitions as a means to enhance its competitive stance. This approach has enabled the business to provide holistic ecosystems and experiences encompassing many devices and services. Furthermore, in light of evolving customer demands that prioritise sustainability and ethical business conduct, Sony's capacity to incorporate environmental awareness into its goods and operational strategies emerges as a distinguishing factor in the competitive landscape. Sony's brand equity and ability to react to emerging trends are crucial factors in determining its competitive position in the ever-evolving business.
Catalysts edit edit source
Sony, established in 1946, has had a trajectory characterized by pioneering advancements, innovative collaborations, and an unwavering commitment to achieving exceptional standards. This section examines the primary factors that have propelled Sony's notable expansion, innovation, and achievement, emphasizing current advancements and their influence on the company's destiny.
1. Technological Innovations
Sony has consistently demonstrated a pioneering spirit in the realm of technical innovation, consistently delivering a range of goods and services that have the ability to redefine and enhance the experiences of consumers.
a) PlayStation Gaming Ecosystem
The PlayStation gaming ecosystem refers to the interconnected network of hardware, software, and online services provided by Sony Interactive Entertainment for the purpose of facilitating gaming experiences on the PlayStation platform. The gaming business underwent a significant transformation when Sony introduced the PlayStation gaming device in 1994. The PlayStation series has seen significant development, resulting in the establishment of a comprehensive ecosystem encompassing many components such as hardware, software, internet services, and virtual reality. Sony has consistently expanded the frontiers of gaming technology through successive iterations, offering engrossing gameplay, visually striking graphics, and interactive encounters that engross players on a global scale. The recent introduction of the PlayStation 5 (PS5) has once again highlighted Sony's dedication to advancing the boundaries of gaming innovation.
b) Imaging and Camera Technologies
Sony's exceptional capabilities in the field of imaging technology have positioned it as a leading force in the domains of photography and videography. The company's range of mirrorless cameras, exemplified by the Alpha series, has received extensive recognition due to their outstanding image quality and innovative functionalities. Sony's imaging sensors play a crucial role in numerous smartphones and other gadgets, highlighting the significant impact the business has on developing the visual technology domain.
c) AI and Robotics Ventures
Sony's dedication to state-of-the-art technology is exemplified by its forays into the fields of artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics. The research and development efforts of the organization have resulted in significant progress in the fields of natural language processing, computer vision, and machine learning. Sony's forays into robotics, exemplified by the Aibo robotic dog, showcase the company's commitment to developing artificial intelligence-driven companions that seamlessly integrate technology and emotion, thereby ushering in novel prospects for human-robot engagement.
2. Entertainment and Content Creation
The entry of Sony into the entertainment business has served as a substantial driver for both expansion and diversity.
a) Television and Film Production
Sony Pictures Entertainment, the company’s film and television production division has produced iconic films and television programs. From the Spider-Man film series to critically acclaimed television series such as "Breaking Bad" and "Better Call Saul," Sony has proven its ability to create content that resonates with global audiences.
b) Sony Music Entertainment, one of the largest music corporations in the world, has significantly shaped the music industry. The company's roster of performers includes some of the most influential names in music and spans multiple musical genres. Sony's position in the industry was strengthened by its acquisition of EMI Music Publishing, allowing it to offer a diverse catalog of music to consumers worldwide.
3. Strategic Collaborations
Sony's strategic alliances and collaborations have been instrumental in fostering innovation and expanding its market presence.
a) Sony and Microsoft Partnership
Sony and Microsoft announced a partnership in 2019 to investigate cloud-based gaming solutions and artificial intelligence technologies. This partnership seeks to utilize Microsoft's Azure cloud platform to improve Sony's streaming and gaming services. The partnership demonstrates Sony's dedication to adapting to shifting market dynamics and investigating new growth opportunities.
b) Sony's Acquisitions and Investments
Sony's portfolio and capabilities have been augmented by its investments and acquisitions of technology firms and innovative companies. Notable examples include the acquisition of the leading anime streaming platform Crunchyroll and the investment in Epic Games, the developer of the popular video game Fortnite. These strategic decisions demonstrate Sony's dedication to remaining at the forefront of the entertainment and technology industries.
4. Financial Strategies
Sony's financial strategies have been crucial to its development and innovation efforts.
a) Diversified Revenue Streams
Sony's diversified business portfolio, which encompasses electronics, gaming, entertainment, and more, has enabled the company to withstand market fluctuations and capitalize on multiple revenue streams. This diversification strategy has provided the company with stability while allowing it to capitalize on emerging consumer trends and preferences.
b) R&D Investments
Research and development (R&D) has been the primary force behind Sony's technological advancements. Consistently allocating significant resources to research and development enables the company to develop innovative products and services that resonate with consumers. Sony's competitive advantage has been strengthened by investments in technologies such as artificial intelligence, image sensors, and audio.
c) Market Penetration (Primary Intensive Growth Strategy)
Sony's principal strategy for intensive growth is market penetration. Sony seeks to increase sales and market share across its diverse product offerings by intensifying its marketing campaigns and attracting more customers. The differentiation strategy facilitates market penetration by developing competitive advantages that appeal to a wide spectrum of consumers in the markets for electronics, gaming, entertainment, and financial services.
5. Investor Confidence and Support
a) Institutional Investors
By holding significant stakes in Sony, significant institutional investors have demonstrated confidence in the company's future. Institutional investors, such as mutual funds and pension funds, have contributed to Sony's growth trajectory by providing financial stability.
b) Individual Investors
Individual investors have responded positively to Sony's innovative products, entertainment offerings, and strategic direction. Individual investors' contributions have not only provided vital capital but also bolstered Sony's standing as an attractive investment option.
Financials edit edit source
Stock Performance edit edit source
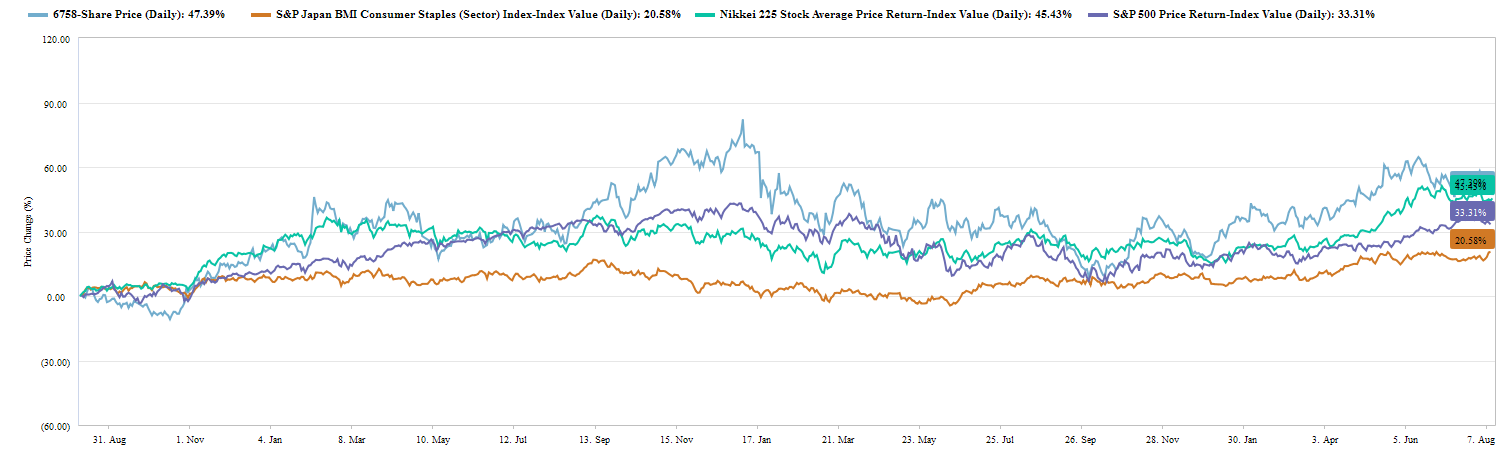
The above graph shows that Sony has outperformed most comparable indexes over the past three years.
Historic edit edit source
| Year end date | 3/30/2020 | 3/30/2021 | 3/30/2022 | 3/30/2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All numbers in thousands of JPY. (¥'000) | ||||
| Revenue | 8,259,885,000 | 8,999,360,000 | 9,921,513,000 | 11,539,837,000 |
| Cost of Revenue | 5,925,049,000 | 6,561,559,000 | 7,219,841,000 | 8,398,931,000 |
| Gross Profit | 2,334,836,000 | 2,437,801,000 | 2,701,672,000 | 3,140,906,000 |
| Operating Expenses: | 1,502,625,000 | 1,469,955,000 | 1,522,979,000 | 1,957,149,000 |
| General & Administrative Expense | 1,502,625,000 | 1,469,955,000 | 1,588,473,000 | 1,969,170,000 |
| Other Operating Expenses | -3,611,000 | - | -65,494,000 | -12,021,000 |
| Operating Income | 832,211,000 | 967,846,000 | 1,178,693,000 | 1,183,757,000 |
| Interest Income | 19,278,000 | 10,457,000 | 19,304,000 | 31,058,000 |
| Interest Expense | 11,090,000 | 12,185,000 | 104,140,000 | 58,951,000 |
| Pretax Income | 799,450,000 | 1,192,370,000 | 1,117,503,000 | 1,180,313,000 |
| Income Tax | 177,190,000 | 995,000 | 229,097,000 | 236,691,000 |
| Net Income | 582,191,000 | 1,171,776,000 | 882,178,000 | 937,126,000 |
| Year end date | 3/30/2020 | 3/30/2021 | 3/30/2022 | 3/30/2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All numbers in thousands of JPY. (¥'000) | ||||
| Assets: | ||||
| Total Assets | 23,039,343,000 | 26,354,840,000 | 30,480,967,000 | 32,041,222,000 |
| Current Assets: | ||||
| Cash And Cash Equivalents | 1,512,357,000 | 1,786,982,000 | 2,049,636,000 | 1,480,900,000 |
| Other Short Term Investments | 1,847,772,000 | 2,902,438,000 | 509,974,000 | 439,307,000 |
| Receivables | 1,191,026,000 | 1,353,393,000 | 1,628,521,000 | 1,777,939,000 |
| Inventory | 589,969,000 | 637,391,000 | 874,007,000 | 1,468,042,000 |
| Prepaid Assets | 594,021,000 | 538,540,000 | - | - |
| Other Current Assets | - | - | 473,070,000 | 610,330,000 |
| Total Current Assets | 5,735,145,000 | 7,218,744,000 | 5,535,208,000 | 5,776,518,000 |
| Non-Current Assets: | ||||
| Net PPE | 1,301,254,000 | 1,362,528,000 | 1,526,643,000 | 1,822,927,000 |
| Goodwill | 783,888,000 | 827,149,000 | 952,895,000 | 1,275,112,000 |
| Other Intangible Assets | 906,310,000 | 996,305,000 | 450,103,000 | 563,842,000 |
| Other Non Current Assets | 767,341,000 | 821,229,000 | 1,631,096,000 | 1,883,828,000 |
| Total Non-Current Assets | 17,304,198,000 | 19,136,096,000 | 24,945,759,000 | 26,264,704,000 |
| Liabilities: | ||||
| Total Liabilities | 18,242,041,000 | 20,725,185,000 | 23,283,718,000 | 24,752,900,000 |
| Current Liabilities: | ||||
| Payables | 2,157,003,000 | 2,521,808,000 | 1,949,334,000 | 2,018,693,000 |
| Current Debt | 839,983,000 | 1,319,567,000 | 2,147,962,000 | 2,102,876,000 |
| Current Deferred Revenue | 2,440,783,000 | 2,773,885,000 | 2,886,361,000 | 3,163,237,000 |
| Other Current Liabilities | 733,732,000 | 1,126,802,000 | 1,776,493,000 | 2,024,130,000 |
| Total Current Liabilities | 6,240,443,000 | 7,815,424,000 | 8,760,150,000 | 9,308,936,000 |
| Non-Current Liabilities: | ||||
| Long Term Debt | 634,966,000 | 773,294,000 | 1,203,646,000 | 1,767,696,000 |
| Long Term Capital Lease Obligation | 314,836,000 | 290,259,000 | 220,113,000 | 192,952,000 |
| Non Current Deferred Liabilities | 549,538,000 | 366,761,000 | 696,492,000 | 356,324,000 |
| Employee Benefits | 324,655,000 | 254,103,000 | 254,548,000 | 236,121,000 |
| Other Non-Current Liabilities | 10,177,603,000 | 11,225,344,000 | 12,368,882,000 | 12,890,871,000 |
| Total Non-Current Liabilities | 12,001,598,000 | 12,909,761,000 | 14,523,568,000 | 15,443,964,000 |
| Equity: | ||||
| Common Stock | 880,214,000 | 880,214,000 | 880,365,000 | 880,365,000 |
| Additional Paid in Capital | 1,289,719,000 | 1,486,721,000 | 1,461,053,000 | 1,463,807,000 |
| Retained Earnings | 2,768,856,000 | 3,857,152,000 | 3,760,763,000 | 4,614,637,000 |
| Treasury Stock | 232,503,000 | 124,228,000 | 180,042,000 | 223,507,000 |
| Minority Interest | 671,996,000 | 53,816,000 | 52,778,000 | 58,613,000 |
| Total Equity | 4,797,302,000 | 5,629,655,000 | 7,197,249,000 | 7,288,322,000 |
| Year end date | 3/30/2020 | 3/30/2021 | 3/30/2022 | 3/30/2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All numbers in thousands of JPY. (¥'000) | ||||
| Operating Cash Flow | ||||
| Net Income from Operating Activities | 622,260,000 | 1,191,375,000 | 1,117,503,000 | 1,180,313,000 |
| Operating Gains/Losses | 96,922,000 | -526,205,000 | 46,468,000 | -13,227,000 |
| Depreciation & Amortisation | 746,451,000 | 663,737,000 | 835,233,000 | 1,004,590,000 |
| Deferred Income Tax | 4,799,000 | -153,427,000 | - | 4,183,000 |
| Other Non-Cash Items | 16,329,000 | -102,215,000 | 695,571,000 | 608,009,000 |
| Change in Working Capital | -157,193,000 | 523,918,000 | -1,191,247,000 | -2,167,113,000 |
| Net Cash Flows from Operating Activities | 1,349,745,000 | 1,350,150,000 | 1,233,643,000 | 314,691,000 |
| Investing Cash Flow | ||||
| Purchase of Property, Plant and Equipment | -439,761,000 | -512,239,000 | -441,096,000 | -613,635,000 |
| Sale of Property, Plant and Equipment | 18,758,000 | 15,823,000 | 11,409,000 | 11,595,000 |
| Purchase of Business | 0 | 0 | -277,618,000 | -283,402,000 |
| Sale of Business | 93,173,000 | 3,151,000 | 64,609,000 | 1,221,000 |
| Purchase of Investment | -1,367,915,000 | -1,734,160,000 | -91,082,000 | -191,129,000 |
| Sale of Investment | 358,196,000 | 469,390,000 | 16,081,000 | 13,548,000 |
| Other Investing Charges | -14,729,000 | -23,481,000 | -11,083,000 | 9,138,000 |
| Net Cash Flows from Investing Activities | -1,352,278,000 | -1,781,516,000 | -728,780,000 | -1,052,664,000 |
| Financing Cash Flow | ||||
| Net Long Term Debt Issuance | -79,608,000 | 308,723,000 | -163,104,000 | 229,578,000 |
| Net Short Term Debt Issuance | 193,332,000 | 355,536,000 | 408,000 | 32,391,000 |
| Common Stock Payments | -200,211,000 | -366,000 | -88,624,000 | -99,248,000 |
| Dividend Payments | -49,574,000 | -61,288,000 | -74,342,000 | -86,568,000 |
| Net Other Financing Charges | 201,719,000 | 64,362,000 | -10,916,000 | 8,147,000 |
| Net Cash Flows from Financing Activities | 65,658,000 | 666,967,000 | -336,578,000 | 84,300,000 |
| Other | ||||
| Beginning Cash Position | 1,473,813,000 | 1,515,295,000 | 1,786,982,000 | 2,049,636,000 |
| Changes in Cash | 63,125,000 | 235,601,000 | 168,285,000 | -653,673,000 |
| Effect of Exchange Rate Changes | -21,643,000 | 36,668,000 | 94,369,000 | 84,937,000 |
| End Cash Position | 1,512,357,000 | 1,786,982,000 | 2,049,636,000 | 1,480,900,000 |
| Capital Expenditure | -439,761,000 | -512,239,000 | -441,096,000 | -613,635,000 |
| Issuance of Debt | 118,447,000 | 1,158,893,000 | 31,866,000 | 394,167,000 |
| Repayment of Debt | -198,055,000 | -494,634,000 | -194,562,000 | -132,198,000 |
| Repurchase of Capital Stock | -200,211,000 | -366,000 | -88,624,000 | -99,248,000 |
| Free Cash Flow | 909,984,000 | 837,911,000 | 792,547,000 | -298,944,000 |
Valuation edit edit source
| ¥ Millions | Historical | Projected | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Income Statement | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 E | 2025 E | 2026 E | 2027 E | 2028 E |
| Revenue | 8,215,880 | 8,105,712 | 7,603,250 | 8,543,982 | 8,665,687 | 8,259,885 | 8,998,661 | 9,921,513 | 11,539,837 | 11,918,278 | 12,255,285 | 12,523,226 | 12,613,100 | 13,095,767 |
| % growth | (1.34%) | (6.20%) | 12.37% | 1.42% | (4.68%) | 8.94% | 10.26% | 16.31% | 3.28% | 2.83% | 2.19% | 0.72% | 3.83% | |
| EBIT | 298,764 | 365,886 | 440,393 | 739,983 | 849,433 | 851,987 | 956,958 | 1,112,396 | 1,179,022 | 1,256,070 | 1,395,280 | 1,488,430 | 1,599,940 | 1,730,733 |
| % of sales | 3.64% | 4.51% | 5.79% | 8.66% | 9.80% | 10.31% | 10.63% | 11.21% | 10.22% | 10.54% | 11.39% | 11.89% | 12.68% | 13.22% |
| Taxes | 88,733 | 94,789 | 124,058 | 151,770 | 45,098 | 177,190 | (45931) | 229,097 | 236,691 | 288,896 | 320,914 | 342,339 | 367,986 | 398,069 |
| % of EBIT | 29.70% | 25.91% | 28.17% | 20.51% | 5.31% | 20.80% | (4.80%) | 20.59% | 20.08% | 23.00% | 23.00% | 23.00% | 23.00% | 23.00% |
| EBIAT | 967,174 | 1,074,366 | 1,146,091 | 1,231,954 | 1,332,665 | |||||||||
| Cash Flow Items | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 E | 2025 E | 2026 E | 2027 E | 2028 E |
| D&A | 354,624 | 397,091 | 327,048 | 361,444 | 374,026 | 416,642 | 687,373 | 835,233 | 1,004,590 | 811,319 | 839,193 | 826,777 | 845,961 | 890,656 |
| % of sales | 4.32% | 4.90% | 4.30% | 4.23% | 4.32% | 5.04% | 7.64% | 8.42% | 8.71% | 6.81% | 6.85% | 6.60% | 6.71% | 6.80% |
| CapEx | (215916) | (375411) | (333509) | (262989) | (312644) | (439761) | (477931) | (441096) | (613635) | 638,704 | 656,832 | 670,751 | 681,903 | 730,158 |
| % of sales | (2.63%) | (4.63%) | (4.39%) | (3.08%) | (3.61%) | (5.32%) | (5.31%) | (4.45%) | (5.32%) | 5.36% | 5.36% | 5.36% | 5.41% | 5.58% |
| Change in NWC | (1201872) | (15040) | (132444) | (126476) | 1,483,159 | 422,805 | (1941143) | 283,028 | 83,527 | 1,072,645 | 1,102,976 | 1,127,090 | 1,135,179 | 1,178,619 |
| % of sales | (14.63%) | (0.19%) | (1.74%) | (1.48%) | 17.12% | 5.12% | (21.57%) | 2.85% | 0.72% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% | 9.00% |
| Free Cash Flow | 1,344,552 | 1,467,415 | 1,516,529 | 1,624,638 | 1,774,860 | |||||||||
| PV of Free Cash Flow | 1,211,308 | 1,190,987 | 1,108,873 | 1,070,200 | 1,053,293 | |||||||||
| Terminal Value | 22,851,318 | |||||||||||||
| Present Value of Terminal Value | 13,561,145 | |||||||||||||
| Enterprise Value | 19,195,805 | |||||||||||||
| (-) Net Debt | 3,151,394 | |||||||||||||
| (-) Minority Interest | 105,939 | |||||||||||||
| Equity Value | 15,938,472 | |||||||||||||
| #Shares | 1,234 | |||||||||||||
| Share Price | 12,916.26 | |||||||||||||
| Sensitivity Analysis | WACC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.5% | 10.0% | 10.5% | 11.0% | 11.5% | 12.0% | 12.50% | ||
| Terminal growth rate | 2.0% | 14,538.39 | 13,436.09 | 12,463.97 | 11,600.34 | 10,828.05 | 10,133.39 | 9,505.26 |
| 2.5% | 15,491.21 | 14,254.75 | 13,173.33 | 12,219.60 | 11,372.25 | 10,614.48 | 9,932.85 | |
| 3.0% | 16,590.61 | 15,190.35 | 13,977.27 | 12,916.26 | 11,980.47 | 11,149.03 | 10,405.45 | |
| 3.3% | 17,335.37 | 15,818.75 | 14,513.23 | 13,377.69 | 12,381.01 | 11,499.25 | 10,713.66 | |
| 3.6% | 18,155.86 | 16,506.05 | 15,095.80 | 13,876.53 | 12,811.97 | 11,874.49 | 11,042.65 | |
| 4.0% | 19,389.09 | 17,529.38 | 15,956.20 | 14,608.16 | 13,440.21 | 12,418.58 | 11,517.44 | |
The above DCF outputs an implied share price of ¥12,916.26. A WACC of 11% and Terminal Growth Rate of 3% was used. As such, the annual required rate of return for an investment in Sony is 11%.
Risk edit edit source
As with any investment, it is crucial to recognise the inherent risks associated with investing in the stock market. This section aims to provide an analysis of the potential risks that may impact the company's performance, and should be considered when making a decision to invest.
Legal and Regulatory Risks edit edit source
Sony Group Corporation's global reach exposes the company to a multitude of legal and regulatory frameworks that influence its operations and market presence.
As governments worldwide intensify their commitment to environmental sustainability, increasing regulations on e-waste management pose a substantial challenge to Sony's consumer electronics and gaming products, which are subject to stricter assessment in terms of their environmental impact and end-of-life disposal. Alongside this, the constant evolution of product safety regulations demands constant attention and adaptation. Compliance with these regulations will require additional efforts and expenses as Sony must dedicate resources to reduce the environmental footprint of its products while ensuring alignment with safety standards.
Sony's operations rely significantly on external business partners for supply, manufacturing, marketing, distribution, and software/network services. Changes in regulations, and policies in both Sony's markets and those of its partners introduces a layer of unpredictability and complexity. These changes could potentially result in challenges within supply chains, operational delays or supplementary costs.
R&D Investment Risks edit edit source
Sony continuously strives to remain competitive through its technological innovations, and the company invests heavily in research and development with plans to spend a total of 760 billion yen on R&D in the current fiscal year, increasing spending by 3% compared to the fiscal year ending March 2023. These investments however, hold a risk to the company if R&D is unsuccessful in producing the results needed to meet ever-changing consumer demands and match intense competition which could to pricing pressures. This may impact Sony's level of profitability and ability to produce new and competitive products and services as scheduled.
Currency and Exchange Rate Risks edit edit source
Sony's operations and financial state may be affected by any fluctuations in foreign exchange rates due to the company's global sales. Sony’s electronics businesses, research and development and headquarters overhead costs are incurred mainly in Yen. Manufacturing and material costs, on the other hand, are incurred mainly in USD and Yen. This implies that any weakening of the Yen’s value against USD could lead to escalated operation costs, consequently impacting Sony's stability over the long term.
The majority of sales are recorded in Yen, USD, Euros, Chinese Yuan. If the Yen strengthens significantly against these foreign currencies it may have an adverse impact on Sony's equity capital, as the incomes from all of its subsidiaries are prepared by translating the local currency of the operating country into Yen.
Market Demand Concerns edit edit source
Sony achieved an impressive 6.3 million PlayStation 5 unit sales in Q1 2023 after the company overcame long-term supply shortages for its flagship gaming console. However, sales in Q2 fell short of expectations as the company reported only 3.3 million units sold during the April-June period and questions arise regarding Sony's capability to reach its 25 million unit sales target for the current fiscal year. Comparatively, Sony's competitor Nintendo achieved 3.9 million sales for their Nintendo Switch Console in Q2 2023, suggesting a shift in consumer preferences towards high-end gaming consoles. Effective marketing strategies, the expansion of PlayStation subscribers, and the launch of significant game titles like Spider-Man 2, will play a pivotal role in propelling Sony's sales momentum forward.
Sony Semiconductor Solutions are a leading supplier of image sensors for smartphone manufacturers, however the company have anticipated the mobile phone market to not recover until at least 2024 due to a slower-than-expected recovery in the Chinese smartphone market and deteriorating conditions in the U.S. market. Sony are set to face a difficult remainder of the financial year as the postponed market recovery could affect demand for Sony's image sensors, a significant contributor to the group's revenue streams.
References edit edit source
Cite error: <ref> tags exist for a group named 'lower-alpha', but no corresponding <references group='lower-alpha'/> tag was found